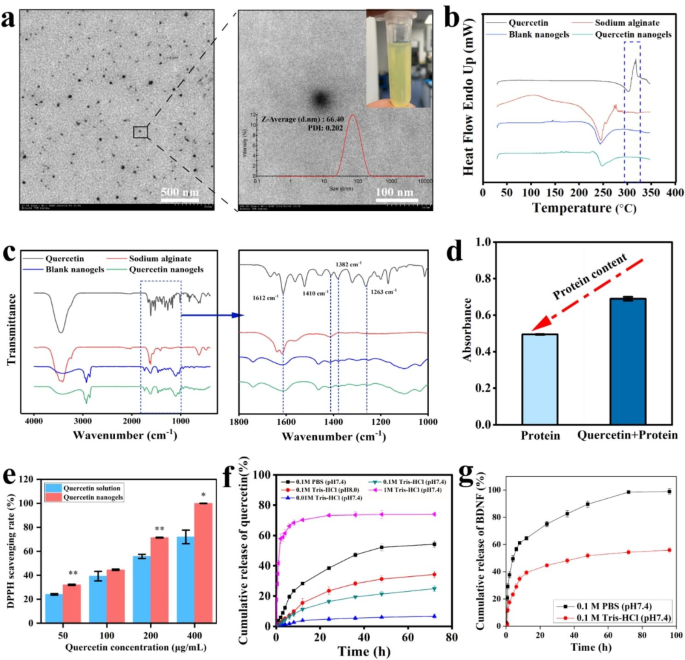
Characterizations of quercetin nanogels and BDNF-Quercetin nanogels
In keeping with the property that divalent cations bridge alginate by chain-chain affiliation, the forming junction zones can encapsulate the poorly soluble drug [22]. Quercetin has vigorous antioxidant actions, however its solubility is poor, leading to low bioavailability. Due to this fact, many nano-preparations, akin to nanofibers [23], nanogels [24], and nanovesicles [25], had been used to enhance their poor bioavailability. To resolve the identical drawback, quercetin nanogels as antioxidant carriers had been ready utilizing zinc alginate based mostly on a part inversion emulsification technique.
Characterization of quercetin nanogels and BDNF-Quercetin nanogels. (a) TEM picture of quercetin nanogels (Left). Scale bar, 500 nm. The magnified TEM picture of quercetin nanogels (Proper). Scale bar, 100 nm. (b) The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) patterns of quercetin nanogels. (c) The Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) of quercetin nanogels. (d) The protecting impact of quercetin on H2O2-induced protein. (e) Antioxidant actions of quercetin nanogels. (f) Cumulative launch profiles of quercetin nanogels. (g) Cumulative launch profiles of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels
The morphology and particle dimension of quercetin nanogels had been noticed utilizing transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and phase-analysis gentle scattering (PALS). The well-formed spherical quercetin nanogels (Fig. 2a), with a particle dimension of 76.34?±?2.34 nm and zeta potentials of -14.48?±?0.90 mV, introduced clear and yellow.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) profiles present priceless insights into the bodily situation of the integrated drug throughout the mix and the composite construction [26]. As depicted in Fig. 2b, quercetin exhibited an endothermic peak concurrent with a melting level at roughly 318 ºC, adopted by an exothermic peak. Contrarily, sodium alginate and quercetin nanogels confirmed no peaks throughout the identical temperature vary. The absence of corresponding peaks within the quercetin nanogels urged that quercetin was efficiently encapsulated into quercetin nanogels, as inferred from the comparative evaluation of the DSC profiles of the three parts. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) was proven in Fig. 2c. The band of quercetin-OH stretching appeared at 3300–3500 cm??1. Quercetin had three sharp peaks, 1410??1 cm, 1382??1 cm, and 1263??1 cm. In the meantime, an analogous peak of quercetin was introduced on the quercetin nanogels, displaying that quercetin was encapsulated into nanogels. By analyzing the characterization of particle dimension, TEM, DSC, FT-IR, Confocal micro-Raman spectroscopy (DetermineS1a), and X-ray diffraction evaluation (Determine S1b), the outcomes demonstrated that quercetin nanogels, as a nanocarrier, had been efficiently ready and quercetin was constructed into alginate nanogels utilizing the tactic of part inversion emulsification. Subsequent, the loading capacities of quercetin and BDNF had been decided utilizing high-performance liquid chromatography and BDNF Emax immunoassay system, respectively. These outcomes demonstrated the profitable encapsulation of quercetin and BDNF throughout the nanogels, with loading capacities of 1.1?±?0.02% and 0.018?±?0.001%, respectively.
It was reported that oxidative stress suppressed and broken the extent of trophic components akin to BDNF [27]. In the meantime, quercetin and its complexes with antioxidant actions had been extensively utilized for medicinal functions [28]. Due to this fact, as an antioxidant, quercetin protects BDNF supply for mind supply. It was indicated in Fig. 2d that protein induced by H2O2 had oxidative injury and a low absorbance when in comparison with protein mixed with quercetin. Quercetin nanogels, in comparison with quercetin resolution, additionally considerably enhance antioxidant capability with growing focus (Fig. 2e). These in vitro outcomes urged that quercetin, significantly quercetin nanogels, could be an antioxidant protein provider that successfully prevents the protein from oxidative injury.
To confirm whether or not quercetin was concerned in developing quercetin nanogels, the discharge habits of quercetin nanogels was investigated utilizing launch media. The cumulative launch charge of quercetin was 24.87?±?1.87% in 0.1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 54.22?±?2.02% in 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4), 34.21?±?2.32% in 0.1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 6.67?±?1.32% in 0.01 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), and 74.03?±?1.32% in 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) (Fig. 2f). The cumulative launch charges had been modulated by various the focus and pH of Tris-HCl, which altered the discharge media’s osmotic stress and ionic focus. These outcomes urged that quercetin was not fully launched from quercetin nanogels. By accumulating the remaining quercetin nanogels within the 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.4) and lysing them with sodium citrate, the quercetin content material was discovered to be roughly 30%. The outcomes confirmed that a part of quercetin participated within the system development of quercetin nanogels, strengthening the cross-linking between molecular chains and making the quercetin nanogels proof against dissolution. The discharge habits of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels is proven in Fig. 2g. After 12 h, the cumulative launch charges of BDNF in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.4) and 0.1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.4) had been 64.58?±?1.29% and 39.40?±?1.65%, respectively, which is as a result of BDNF is extra water-soluble and may freely diffuse into the discharge media. Lastly, the cumulative launch charge of BDNF reached 98.93?±?1.98% in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7.4) and 55.87?±?1.99% in 0.1 M Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), respectively, displaying that monovalent cations of the discharge medium facilitate the discharge of BDNF. Total, quercetin nanogels primarily launch BDNF by free diffusion and ion trade within the launch medium.
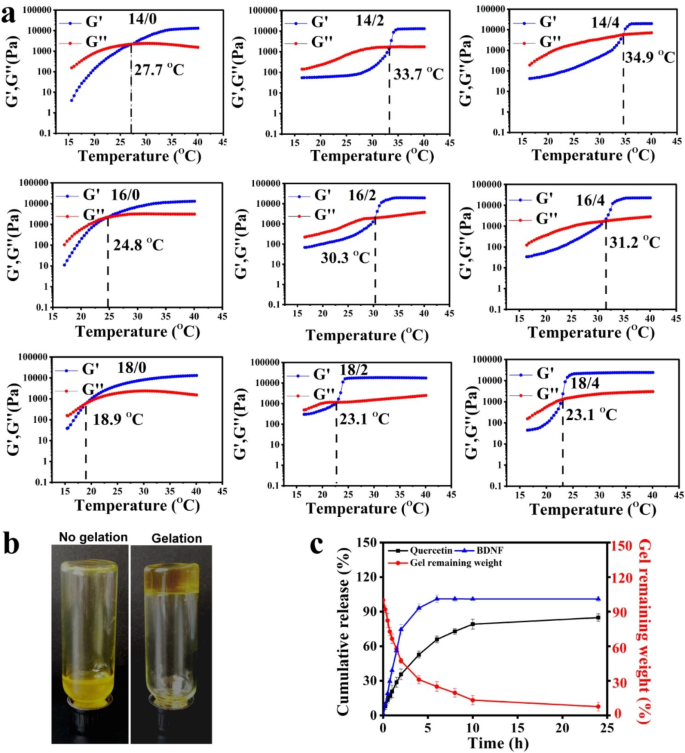
Characterization of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel
In keeping with our earlier research, the nanogels-based thermosensitive hydrogel facilitates the development of the antidepressant results of the drug by immobilizing the therapeutic brokers domestically within the nasal cavity and releasing them constantly [29, 30]. Therefore, the temperature-sensitive property of quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel was investigated by rheological evaluation, which indicated the results of poloxamer 407 (P 407) and P 188 on gelling temperature. The loss modulus (G’’) dominated storage modulus (G’), which urged that thermosensitive gel was flowing, conversely forming an entangled community and viscous-like gels. For quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel, the loss and storage modulus had the identical modulus as gelling temperature, such that G? was virtually equal to G? [31]. It was noticed in Fig. 3a that gelling temperature with elevated P 407 had a decreased tendency, however P 188 was the alternative. The G? at about 30 °C introduced a dramatic lower, indicating the solution-gelation transition of quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel. Gelation temperature tailored to intranasal supply when P 407 and P 188 closed to the ratio of 16 to 2, roughly 30.3 ºC. Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel introduced a flowing state at 25 ?, whereas a non-flowing type at 37 ? (Fig. 3b).
The characterization of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel. (a) Rheological habits of quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel (P 407 / P 188, w/w). (b) The looks of quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel. (c) Cumulative launch profiles from BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel
The discharge behaviors of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel had been investigated by PBS (pH 7.4). Cumulative launch profiles and becoming evaluation had been indicated in Fig. 3c and Desk S1, respectively. The discharge kinetics of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels had been analyzed by computing the kinetic fixed. The discharge kinetics of quercetin and BDNF had been discovered to obey the first-order launch curve, following the Ritger-Peppas mannequin. These outcomes indicated that the remaining BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel slowly decreased as BDNF and quercetin had been launched sustainably with non-Fick’s diffusion. Till 24 h, BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel had been totally degraded, and each parts had been launched fully from the nanogels.
Cell biology analysis and immune response
The in vitro cell viability was evaluated utilizing Calcein-AM labeled fluorescence assay to evaluate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated and regular RAW264.7 cells handled with quercetin, clean nanogels, and quercetin nanogels (Determine S2a). The enlarged cell quantity and the modified cell morphology had been noticed after LPS stimulation in contrast with the management. Quercetin, clean nanogels, and quercetin nanogels had no cytotoxic results in comparison with the management and exhibited nonsignificant results on cell viability. In Determine S2b, the proliferative results of quercetin nanogels on RAW264.7 cells rising had been analyzed by the producer’s directions of the BrdU ELISA package. The outcomes indicated that quercetin, clean nanogels, and quercetin nanogels had no vital results on the proliferation of RAW264.7 cells till 24 h.
Immune cells can produce some cytokines important to regulating the immune response. Nonetheless, irregular cytokines might result in immune-mediated problems, together with allergic reactions, infectious illnesses, cancers, and autoimmunity. The earlier examine confirmed that inspecting the results of nanogels on cytokine ranges was worthwhile for immune programs induced by immune stimulators [32]. Pure energetic compounds have been extensively utilized in treating illnesses attributable to their low toxicity and good biocompatibility [33,34,35]. To analyze whether or not quercetin nanogels had immunostimulatory results, TNF-? and IL-6 concentrations within the cell supernatant had been decided after incubation with RAW 264.7 cells for 48 h. In contrast with the management, quercetin nanogels and clean nanogels didn’t stimulate RAW 264.7 cells to secrete extreme inflammatory components (Determine S2c-d), indicating that the quercetin nanogels and clean nanogels didn’t activate the mobile immune response.
Analysis of in vitro anti-inflammatory actions
The anti-inflammatory exercise of quercetin nanogels is evaluated by LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. It was discovered that in contrast with clean nanogels, quercetin nanogels successfully restricted inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA expression, additional inhibiting overproduction of nitric oxide (NO) that the iNOS produced, and at last curbing the technology of nitrite, one of many merchandise of nitric oxide (Determine S3a-c). These outcomes confirmed that quercetin nanogels enhanced cell survival and may have an affect on the end result of depressive dysfunction brought on by irritation, according to earlier research [36]. In comparison with the LPS group, quercetin nanogels down-regulated the expression of iNOS, NO, and nitrite, higher than pure quercetin. In the meantime, cytokines, the vital biomarkers of nanocarrier immunotoxicity, have been extensively utilized in immunotoxicity research [37]. Specifically, the secretion of TNF-? and IL-6 in RAW 264.7 cells elevated in response to irritation, enjoying a pivotal function in lowering irritation ranges. As proven in Determine S3d-g, LPS up-regulated the mRNA and protein expression of TNF-? and IL-6 in RAW 264.7 cells. Nevertheless, quercetin and quercetin nanogels considerably inhibited TNF-? and IL-6 mRNA expression and protein expression, with quercetin nanogels outperforming quercetin.
Usually, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) exercise in regular tissue cells was poor, whereas COX-2 stage in inflammatory cells would enhance a number of occasions when irritation stimulated cells. This elevation in prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), in flip, exacerbates the inflammatory response and induces tissue injury. Each COX-2 and PGE2 play pivotal roles on this inflammatory course of. In contrast with the LPS group, mRNA expression ranges and protein expression of COX-2 and its downstream product, PGE2, had been considerably up-regulated in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells (Determine S3h-j). Conversely, each quercetin and quercetin nanogels confirmed vital inhibitory results on mRNA expression and protein expression of COX-2 and PGE2 content material. Whereas clean nanogels didn’t exhibit vital anti-inflammatory results in comparison with the LPS group, quercetin nanogels markedly inhibited the COX-2/PGE2 signaling pathway response. Total, quercetin nanogels, in comparison with free quercetin, successfully inhibited the over-expression of inflammatory genes, together with iNOS, IL-6, TNF-?, COX-2, and PGE2. Quercetin nanogels reveal glorious biocompatibility and augmented anti-inflammatory properties, thus positioning them as promising nanocarriers for treating despair and different inflammation-associated illnesses.
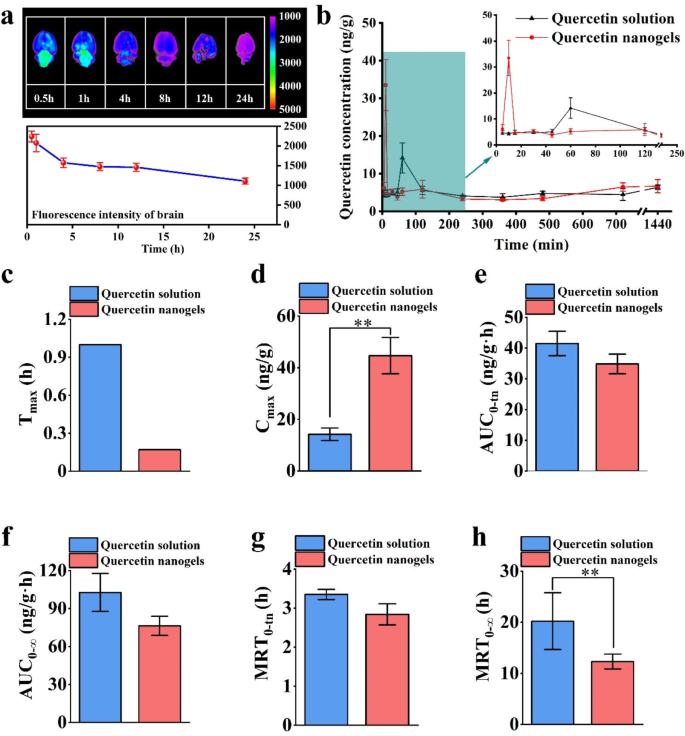
In vivo biodistribution and pharmacokinetics research
In vivo biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of quercetin nanogels had been evaluated utilizing Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. Mind tissues and plasma evaluation had been carried out at totally different durations after intranasal administration of quercetin nanogels. To evaluate their mind biodistribution, rhodamine B isothiocyanate (RBITC)-labeled quercetin nanogels had been administrated, and the fluorescence was analyzed. It was present in Fig. 4a that essentially the most intense fluorescence within the rat mind was noticed roughly 30 min post-administration, adopted by a gradual lower. Quercetin nanogels had been rapidly delivered to the mind area and predominantly amassed within the mind at brief time scales, suggesting their potential for focused mind supply through the intranasal route, which may very well be helpful for treating depressive problems. To guage whether or not the quercetin nanogels improved in vivo bioavailability of quercetin, the corresponding plasma focus vs. time (Fig. 4b) and pharmacokinetic parameters (Fig. 4c-h) of the orally administrated quercetin and intranasally administrated quercetin nanogels had been analyzed, respectively. The focus vs. time curve of quercetin nanogels confirmed a pointy enhance at roughly 15 min. In distinction, oral administration of the quercetin reached a most plasma focus of 4 h post-administration, leading to a slower enhance than quercetin nanogels. The intranasally administered quercetin nanogels exhibited a shorter Tmax and better Cmax than orally administered quercetin, indicating speedy achievement of peak drug focus. Moreover, the bioavailability of the intranasally administered quercetin nanogels was practically 50 occasions higher than that of orally administered quercetin, as decided by relative bioavailability calculations. Due to this fact, the quercetin nanogels present the potential to beat BBB and improve quercetin bioavailability at decrease doses.
Distribution in mind and pharmacokinetic examine of quercetin nanogels. (a) Fluorescence evaluation of quercetin nanogels within the mind. (b) Hippocampal quercetin concentration-time curves after intragastric or intranasal supply. Pharmacokinetic parameters embrace (c) Tmax (h), (d) Cmax (ng/g), (e) AUC0???tn (ng/g·h), (f) AUC0?? (ng/g·h), (g) MRT0??(h), (h), MRT0???tn(h). **p?<?0.01 in contrast with the orally administrated quercetin resolution
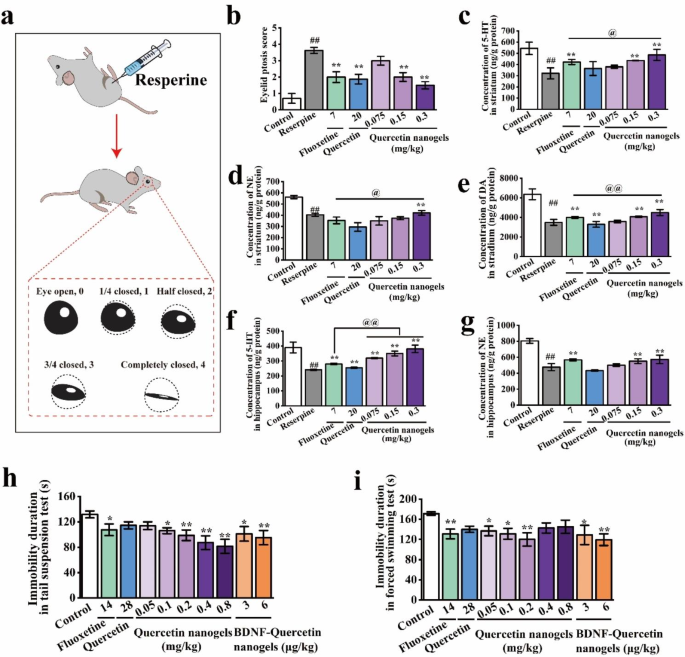
The antidepressant actions of quercetin nanogels and their BDNF supply
To analyze the potential antidepressant actions of quercetin nanogels, we examined the hypotheses utilizing two fashions that contained intraperitoneal injection of reserpine and a well-established behavioral despair mannequin. The analysis findings indicated that reserpine’s mechanism of motion concerned the depletion of biogenic amines. A considerable dose of reserpine resulted within the depletion of noradrenaline, adrenaline, dopamine, and 5-HT within the mind for a length exceeding 7 days. Nevertheless, depressive habits continued for under 3 days [38]. Concurrently, the reserpine-induced mannequin was chosen attributable to its easy process and excessive success charge, making it an appropriate alternative for evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of antidepressants. A schematic diagram of the ptosis rating of rats decreased by reserpine was indicated in Fig. 5a. It was used to evaluate the rats’ depression-like state induced by reserpine. The outcomes urged that the eyelid ptosis rating of the administrated medication was considerably decrease than the mannequin group induced by reserpine. Additionally, quercetin nanogels considerably alleviated the depletion of 5-HT, NE, and DA within the striatum and hippocampus (Fig. 5b-g), suggesting that quercetin nanogels successfully restrained on reserpine-induced depletion of monoamine neurotransmitters.
The antidepressant actions of quercetin nanogels and their BDNF supply. (a) Schematic diagram of ptosis rating of rats decreased by reserpine. (b) Eyelid ptosis rating of rats. (c) 5-HT focus within the striatum. (d) NE focus within the striatum. (e) DA focus within the striatum. (f) 5-HT focus within the hippocampus. (g) NE focus within the hippocampus. (h) Immobility length of mice in tail suspension check. (i) Immobility length of mice in a compelled swimming check. ##p?<?0.01 in contrast with the management group. *p?<?0.05, **p?<?0.01 in contrast with the reserpine group. @p?<?0.05, @@p?<?0.01 in contrast with fluoxetine
Behavioral assessments are used to evaluate the behavioral traits after intranasal administration, together with the open subject check (OFT), tail suspension check (TST), and compelled swimming check (FST). The OFT was used to evaluate general exercise, anxiety-related habits, and locomotor exercise in a novel surroundings to rule out any inhibitory or excitatory results of BDNF-quercetin nanogels [39]. The TST and FST had been extensively carried out to research antidepressant actions and depression-like habits of antidepressant medication [40, 41]. Within the OFT of the mice, the numerous variations weren’t found within the rearing occasions and whole distance, as proven in Determine S4a-b, in comparison with the management group, suggesting that the medication had no impression on the examined mice. Within the TST and FST (Fig. 5h-i), low doses of quercetin nanogels and BDNF-Quercetin nanogels considerably decreased the immobility length, thereby enhancing depressive habits and demonstrating superior antidepressant results in comparison with different teams.
A preliminary examine utilizing two fashions manifested that BDNF-Quercetin nanogels had higher antidepressant actions and had been virtually equal to the orally administrated fluoxetine and quercetin. Nonetheless, a dose of the previous was decrease, displaying their superiority of mind focusing on by intranasal supply.
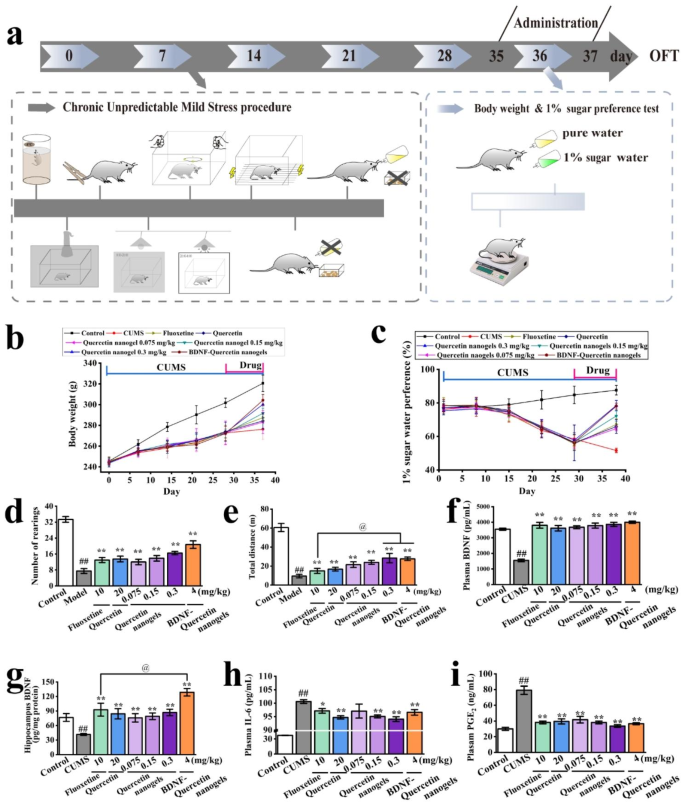
Antidepressant results of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel on the persistent unpredictable delicate stress (CUMS) rats
The CUMS mannequin (Fig. 6a) was additional carried out to review the antidepressant mechanism of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels after the preliminary analysis of antidepressant exercise utilizing two animal fashions. It was noticed that CUMS-induced weight reduction and anhedonia had been considerably mitigated by the experimental medication, significantly BDNF-Quercetin nanogels, demonstrating a greater impact on the pressured rats (Fig. 6b-c). The OFT was used to evaluate the exploratory habits of the drug-treated CUMS rats after administration. It was indicated that fluoxetine, quercetin, quercetin nanogels, and BDNF-quercetin nanogels elevated the variety of rearings and the entire distance of CUMS mannequin (Fig. 6d-e). Each BDNF-quercetin nanogels and quercetin nanogels demonstrated extra vital antidepressant results than fluoxetine, as evidenced by the entire distance. Plasma and hippocampal BDNF concentrations of the CUMS rats had been markedly enhanced by the experimental medication. Notably, the hippocampal BDNF stage within the BDNF-Quercetin nanogel group exhibited a major change in comparison with the fluoxetine group. These findings urged that the supply of exogenous BDNF compensated for the lack of BDNF within the mind (Fig. 6f-g), thereby enhancing its antidepressant results.
Medical studies and meta-analyses discovered that depressed sufferers had vital hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis hyperactivation. These dysfunctions elevated the stress hormone cortisol secretion and inflammatory biomarkers’ ranges [42,43,44,45,46]. It was proven in Determine S5a-c that the degrees of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH), and corticosterone in rats had been considerably elevated by CUMS. Nevertheless, the one stage of corticosterone was decreased significantly by BDNF-Quercetin nanogels in comparison with CUMS rats. Many research have discovered that testosterone had antidepressant results in socially remoted male however not feminine rats [47]. It was noticed in Determine S5d that quercetin nanogels, in a dose-dependent method, improved the testosterone stage, and BDNF-Quercetin nanogels additionally confirmed a major enhance in comparison with CUMS rats. Within the meantime, irritation was a vital organic occasion that may enhance the danger of main depressive problems. CUMS-induced rats exhibited larger IL-6 and PGE2 ranges in plasma (Fig. 6h-i). Inflammatory ranges of the rats had been decreased after administration. BDNF-Quercetin nanogels additionally introduced vital variations in comparison with these with out administration. In abstract, BDNF-Quercetin nanogels at a decrease dose decreased the irregular habits of CUMS mannequin and improved their biochemical indicators.
Antidepressant results of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels on the CUMS rats. (a) Schematic diagram of the CUMS process. (b) Modifications in physique weight of rats. (c) Modifications of 1% sucrose choice of rats. (d) Variety of rearings. (e) Complete distance of rats. (f) BDNF focus in plasma. (g) BDNF content material within the hippocampus. (h) IL-6 focus in plasma. (i) PGE2 content material within the hippocampus. ##p?<?0.01 in contrast with the management group. *p?<?0.05, **p?<?0.01 in contrast with CUMS mannequin. @p?<?0.01 in contrast with the fluoxetine
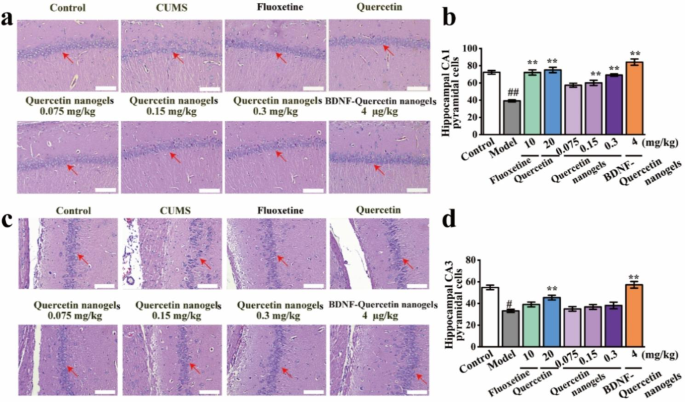
Pathological modifications in rat hippocampal tissues. (a) Pathological modifications of CA1 subregion in rat hippocampal tissues (scale bar: 100 ?m). (b) Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. (c) Pathological modifications of CA3 subregion in rat hippocampal tissues (scale bar: 100 ?m). (d) Hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. ##p?<?0.01 in contrast with the management group. *p?<?0.05, **p?<?0.01 in contrast with CUMS mannequin
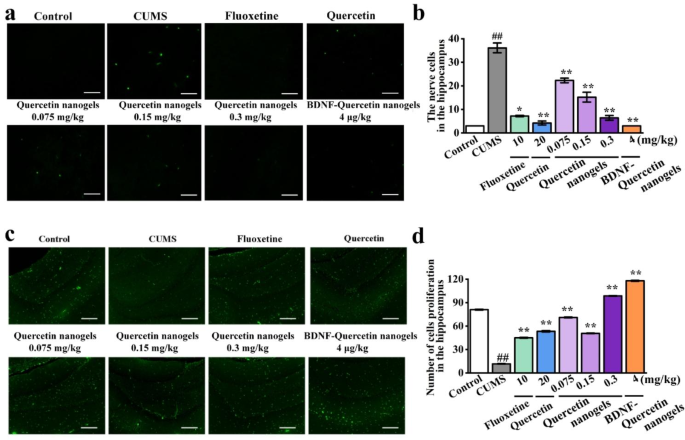
Results of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells had been investigated. It was noticed within the H&E staining that there was dramatic injury to pyramidal cells within the hippocampal subregion of CUMS rats (Fig. 7a-d). In comparison with CUMS mannequin, these abnormalities had been considerably improved by BDNF-Quercetin nanogels. Equally, cell apoptosis and proliferation had been additionally noticed and analyzed by TUNEL and Ki67 staining, respectively. The variety of constructive cells in CUMS rats considerably decreased (Fig. 8a-d). BDNF-Quercetin nanogels considerably elevated the corresponding constructive cells. On the identical time, these impairments of pyramidal cells had been additionally discovered within the prefrontal cortex of CUMS rats (Determine S6), and BDNF-Quercetin nanogels confirmed the identical therapeutic results as within the hippocampus.
CUMS-induced cell apoptosis and proliferation within the hippocampus of rats. (a) TUNEL staining. (b) The nerve cells by TUNEL staining. (c) Ki67 staining. (d) Variety of cell proliferation by Ki67 staining. ##p?<?0.01 in contrast with the management group. *p?<?0.05, **p?<?0.01 in contrast with the CUMS mannequin
Apoptosis is a vital mechanism of CUMS-induced despair [48]. As an anti-apoptotic endogenous membrane protein, B cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) prevents cells from coming into the apoptotic program. B-cell lymphoma extra-large (Bcl-xL), like Bcl-2, is one other antiapoptotic issue supporting neuronal survival however not selling axon regeneration. BCL2-associated X (Bax) was a pro-apoptotic protein selling cells to enter apoptosis. The examine findings indicated that CUMS elevated Bax mRNA expression within the hippocampal and prefrontal cortex tissues (Determine S7a, b) and selectively decreased hippocampal Bcl-xL mRNA ranges (Determine S7c, d) with out altering Bcl-2 mRNA expression (Determine S7e, f).
BDNF-quercetin nanogels exerted antidepressant results on CUMS rats, primarily by anti-stress, anti-inflammation, and neuroprotection. BDNF-quercetin nanogels can restore HPA axis operate, inhibit neuron cell apoptosis, and promote neuron cell regeneration. To elucidate the impression of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels on CUMS rats, a complete, built-in omics strategy was used to research potential antidepressant mechanisms.
Antidepressant mechanism of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel on the CUMS rats
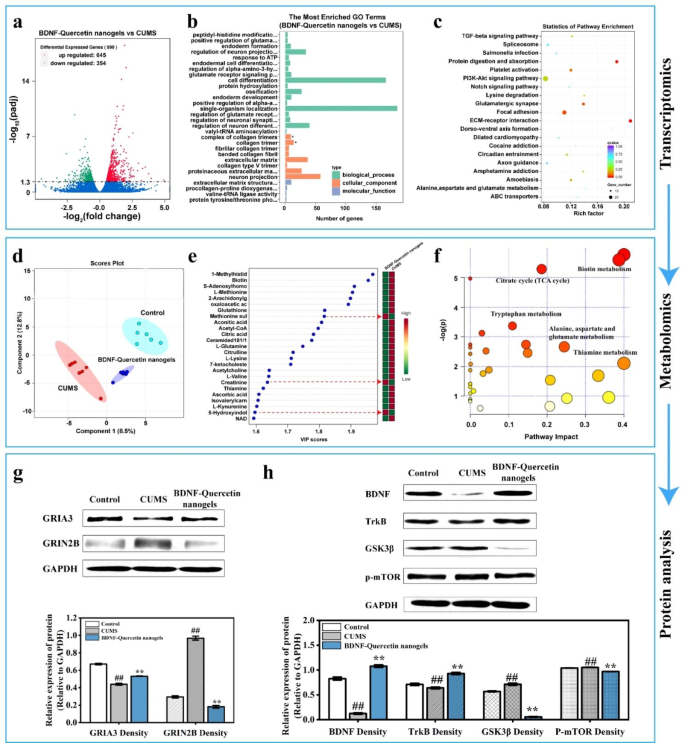
Gene expression of whole mRNA remoted from rat hippocampus was assessed utilizing RNA sequencing. The transcriptomic volcano map revealed that in comparison with CUMS group, 999 genes had been differentially expressed within the BDNF-quercetin nanogels group, with considerably up-regulated 645 genes and considerably down-regulated 354 genes (Fig. 9a). Probably the most enriched GO phrases in Fig. 9b introduced that BDNF-quercetin nanogels modified organic processes (together with peptidyl-histidine modification and constructive regulation of glutamate receptor), mobile parts (together with a fancy of collagen trimers), and molecular operate (extracellular matrix structural constituent) of CUMS rats. Gene set enrichment evaluation (GSEA) was subsequent carried out utilizing the KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database, revealing vital enrichment together with TGF-? and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, glutamatergic synapse, alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism (Fig. 9c). Moreover, GO phrases related to antioxidant exercise had been recognized in Desk S4. Oxidative phosphorylation was additional present in KEGG pathway enrichment evaluation. In keeping with earlier research on despair, it was discovered that there are glutamate receptor-related phrases, PI3K-Akt, glutamatergic synapse, and glutamate metabolism signaling pathways. These transcriptomic findings urged that BDNF-Quercetin nanogels not solely induced antioxidant actions through oxidative phosphorylation but additionally exerted antidepressant results on CUMS rats by enhancing the glutamatergic system and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. A metabolomic evaluation was then carried out to research the modifications in hippocampal metabolites. Partial least sq. evaluation (PLS-DA) in Fig. 9d indicated that the affect of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels on metabolites neared the management and differed from CUMS group, displaying that management, CUMS, and BDNF-Quercetin nanogels had a major distinction within the ranges of whole metabolites. Additional evaluation in Fig. 9e confirmed that in comparison with CUMS group, some metabolites (together with methionine sulfoxide, creatinine, 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid) had been up-regulated, whereas others (together with 1-Methylhistidine, biotin, 2-Arachidonylglycerol, S-Adenosylhomocysteine, Acetyl-CoA, 7-ketocholesterol, Ascorbic acid, L-Methionine) had been down-regulated. The metabolic pathways related to the antidepressant results primarily encompassed the next biochemical course of: (1) biotin metabolism; (2) citrate cycle; (3) tryptophan metabolism; (4) Alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism; (5) thiamine metabolism (Fig. 9f). Taken collectively, transcriptomic and metabonomic information confirmed that the glutamatergic system and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway had been the first antidepressant mechanism of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels in CUMS rats.
Western blot experiments had been carried out to confirm associated protein expression. Protein expression of the glutamatergic system was demonstrated in Fig. 9g. These outcomes introduced that persistent stress considerably decreased the GRIA3 (the receptor of AMPA) protein content material and elevated the GRIN2B (the receptor of NMDA) protein content material within the hippocampus of rats. Furthermore, BDNF-Quercetin nanogels regulated the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway by enhancing the irregular expression of BDNF, TrkB, GSK3?, and p-mTOR after CUMS (Fig. 9h). These outcomes confirmed that exogenously supplemented BDNF may bind to its receptor TrkB and additional activate the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, thereby regulating the expression of irregular GSK3? and p-mTOR proteins.
In abstract, the protecting results of quercetin nanogels on BDNF had been achieved by antioxidant actions related to oxidative phosphorylation. By integrating omics prediction and protein expression verification, the outcomes confirmed that BDNF-Quercetin nanogels exerted antidepressant results on CUMS rats by modulating the glutamatergic system and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.
Antidepressant mechanism of BDNF-Quercetin nanogels within the thermosensitive gel on the CUMS rats. (a) Volcano map. (b) GO enrichment evaluation. (c) KEGG pathway enrichment evaluation of BDNF-quercetin nanogels vs. CUMS mannequin. (d) Partial least squares-discriminant evaluation (PLS-DA). (e) VIP evaluation. (f) Main metabolic pathways that BDNF-Quercetin nanogels enhance CUMS rats. (g-h) Expression of GRIA3, BDNF, TrkB, P-mTOR, GRIN2B, and GSK3? within the hippocampus of rats. ##p?<?0.01 in contrast with the management group. **p?<?0.01 in contrast with the CUMS group