Excessive-temperature superconductors, exemplified by supplies like Bi-2223, have lengthy grappled with limitations similar to low essential present density and insufficient magnetic flux pinning.
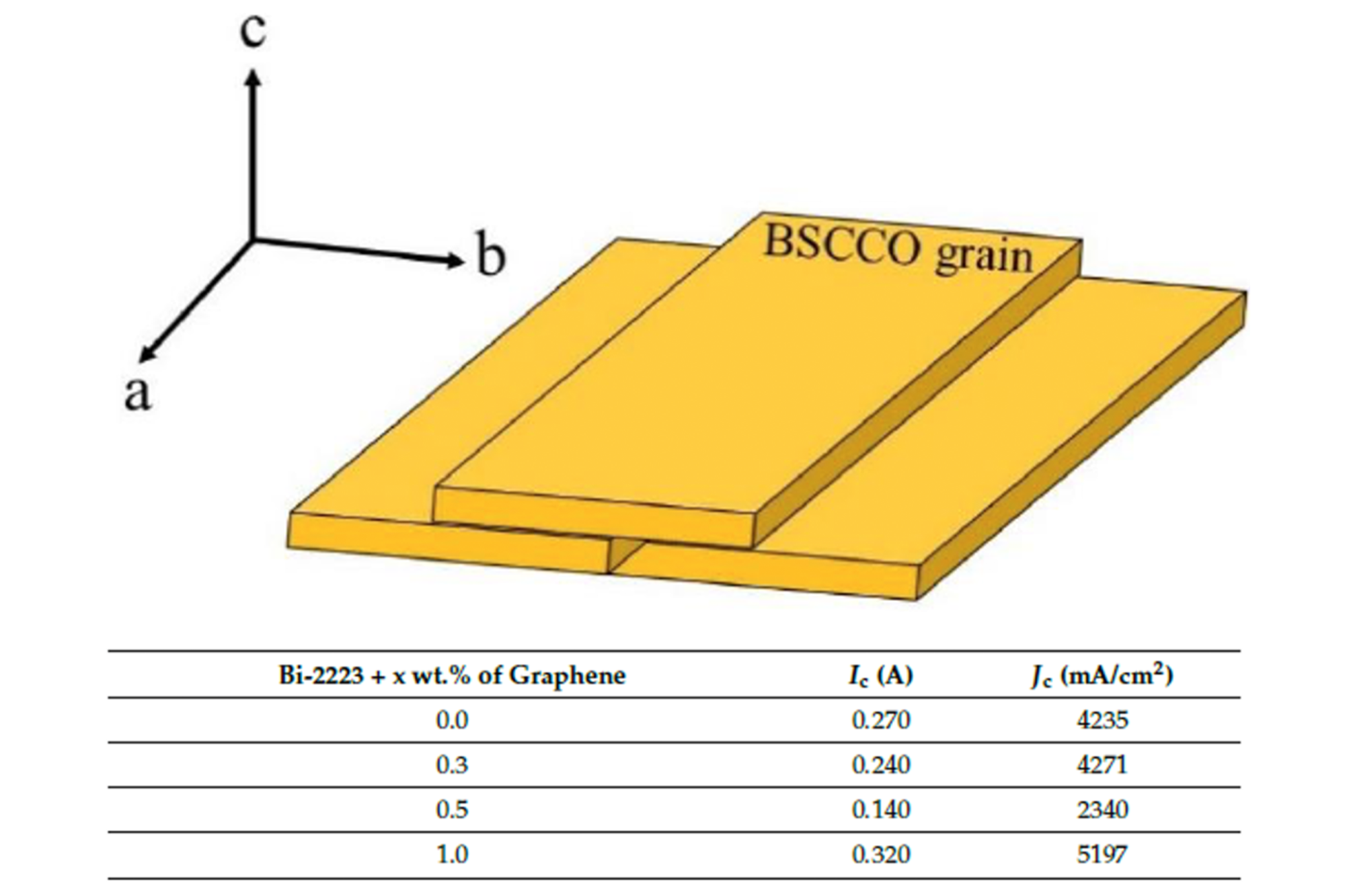
Variation of the essential present density of Bi-2223 (a bismuth strontium calcium copper oxide) with graphene addition. (High) Schematic diagram demonstrating the parallel alignment of the BSCCO grain to its ab-plane. (Backside) The desk highlights that the Bi-2223 high-temperature superconductor pattern with 1.0 weight % graphene displays the best essential present density (Jc). Picture Credit score: Muralidhar Miryala from SIT, Japan
Moreover, their intricate synthesis course of has posed challenges to their development. In a current examine, a global staff of researchers has demonstrated that by introducing graphene nanoparticles into bulk Bi-2223 utilizing the co-precipitation technique, it’s doable to reinforce the essential present density. This breakthrough opens up new avenues for future analysis and improvement within the area of Bi-2223 superconductors.
Superconductors are substances that exhibit zero electrical resistance when cooled beneath a selected essential temperature. Typically, superconductors possess a really low essential temperature, usually near absolute zero. Nonetheless, there exists a class of superconductors known as high-temperature superconductors (HTS) which have a essential temperature exceeding 77 Okay, which is the boiling level of liquid nitrogen.
HTS supplies have discovered intensive purposes in numerous industries for the creation of superconducting gadgets attributable to their capability to function at comparatively increased temperatures in comparison with typical superconductors.
Bismuth strontium calcium copper oxide, generally often called BSCCO, belongs to the category of HTS and has been extensively researched and utilized throughout numerous fields, together with engineering, medical tools, mining, and transportation methods. Inside this class, (Bi1.6Pb0.4)Sr2Ca2Cu3O10, also referred to as Bi-2223, stands out for having the best superconducting essential temperature, making it a topic of serious curiosity for potential purposes.
Nonetheless, the event and development of Bi-2223 superconductors have confronted challenges. These embody limitations similar to low essential present density, subpar magnetic flux pinning capabilities, and a posh synthesis course of. These hurdles have impeded the progress in harnessing the complete potential of Bi-2223 superconductors.
In an effort to beat these challenges, a staff of researchers, underneath the management of Professor Muralidhar Miryala from the Supplies for Power and Environmental Laboratory of Superconducting Supplies at Shibaura Institute of Know-how, and Professor Awang Kechik Mohd Mustafa from the Division of Physics within the School of Science at Universiti Putra Malaysia, carried out a examine to discover the affect of including graphene nanoparticles on the part formation and superconducting traits of Bi-2223.
On this examine, we report the results on the essential temperature, essential present density, and structural and morphological properties of Bi-2223, when graphene nanoparticles are built-in into them utilizing a novel co-precipitation technique.
Muralidhar Miryala, Professor, Supplies for Power and Environmental Laboratory of Superconducting Supplies, Shibaura Institute of Know-how
This analysis was printed within the Nanomaterials journal on July 28th, 2023. The examine encompasses a collaborative effort by a staff of co-authors, together with Abdullah Siti Nabilah, Nursyahirah Kamarudin Aliah, Soo Kien Chen, Kean Pah Lim, Abdul Karim Muhammad Khalis, and Shaari Abdul Halim from Universiti Putra Malaysia, Abidin Talib Zainal from Jeonbuk Nationwide College, Baqiah Hussein from Dezhou College, in addition to Hashim Azhan and Ermiza Suhaimi Nurbaisyatul from Universiti Teknologi MARA Pahang.
Given the distinctive electrical, mechanical, and chemical attributes of graphene, together with the sheet-like microstructures widespread to each graphene and Bi-2223, the inclusion of graphene nanoparticles as components presents an intriguing prospect. Of their examine, the analysis staff scrutinized the part formation and crystal constructions of distinct Bi-2223 samples containing 0.3, 0.5, and 1.0 weight % graphene nanoparticles. This evaluation was carried out utilizing X-Ray diffraction (XRD) and in contrast in opposition to a pure Bi-2223 pattern. Moreover, they assessed the essential temperature of those samples utilizing the alternate present susceptometry (ACS) technique.
The X-Ray diffraction (XRD) findings unveiled the presence of a predominant Bi-2223 part alongside a secondary Bi-2212 part, which is one other member of the BSCCO household, in all of the samples examined. Notably, the amount fraction occupied by the Bi-2223 part was increased in samples containing 0.3 and 0.5 weight % graphene, however barely decrease within the pattern with 1.0 weight % graphene.
Moreover, the ACS evaluation confirmed that essential temperature-related parameters, together with the onset essential temperature, part lock-in temperature, and coupling peak temperature, all indicators of superconducting efficiency, decreased because the graphene content material elevated.
Surprisingly, the pattern containing 1.0 weight % graphene exhibited the best essential present density and demonstrated essentially the most appropriate microstructure for the event of Bi-2223 superconductors.
These outcomes recommend that the addition of graphene nanoparticles, appearing as impurities, have the potential to reinforce the present density of Bi-2223 superconductors.
Muralidhar Miryala, Professor, Supplies for Power and Environmental Laboratory of Superconducting Supplies, Shibaura Institute of Know-how
Describing potential future purposes for Bi-2223 superconductors with improved present density, Prof. Miryala notes, “These superconductors have the potential to facilitate various fields, similar to MRI imaging, energy era and distribution, renewable power integration, transportation and aerospace, particle accelerators, electronics and quantum computing, environmental sustainability, industrial and manufacturing processes, and academic and scientific outreach.”
Journal Reference
Abdullah, S. N., et al. (2023). Microstructure and Superconducting Properties of Bi-2223 Synthesized through Co-Precipitation Technique: Results of Graphene Nanoparticle Addition. Nanomaterials. doi.org/10.3390/nano13152197.
Supply: https://www.shibaura-it.ac.jp/en
