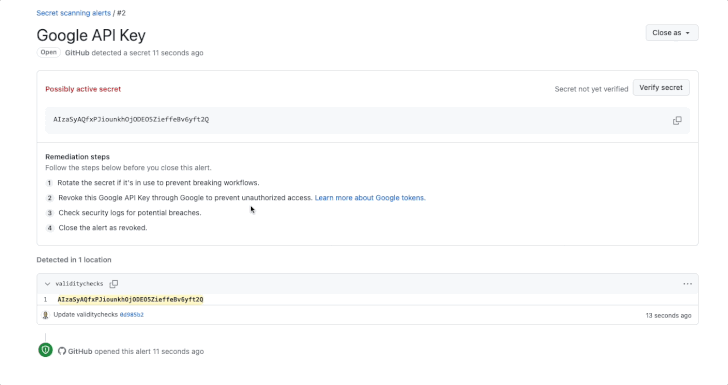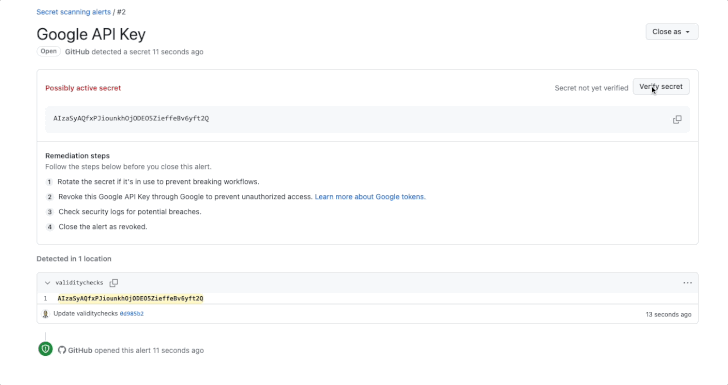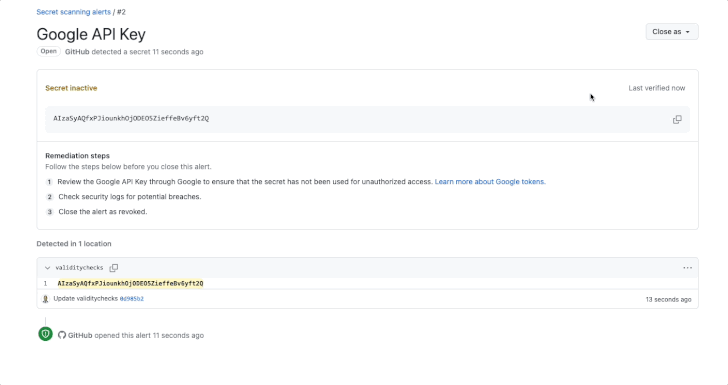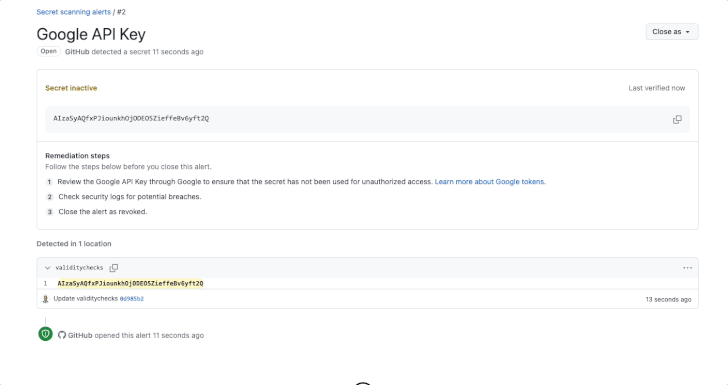
GitHub has introduced an enchancment to its secret scanning function that extends validity checks to common providers akin to Amazon Internet Companies (AWS), Microsoft, Google, and Slack.
Validity checks, launched by the Microsoft subsidiary earlier this 12 months, alert customers whether or not uncovered tokens discovered by secret scanning are lively, thereby permitting for efficient remediation measures. It was first enabled for GitHub tokens.
The cloud-based code internet hosting and model management service stated it intends to help extra tokens sooner or later.
To toggle the setting, enterprise or group homeowners and repository directors can head to Settings > Code safety and evaluation > Secret scanning and examine the choice “Robotically confirm if a secret is legitimate by sending it to the related associate.”
Earlier this 12 months, GitHub additionally expanded secret scanning alerts for all public repositories and introduced the availability of push safety to assist builders and maintainers proactively safe their code by scanning for extremely identifiable secrets and techniques earlier than they’re pushed.
The event comes as Amazon previewed enhanced account safety necessities that can implement privileged customers (aka root customers) of an AWS Group account to modify on multi-factor authentication (MFA) beginning in mid-2024.
“MFA is without doubt one of the easiest and simplest methods to reinforce account safety, providing an extra layer of safety to assist forestall unauthorized people from having access to techniques or information,” Steve Schmidt, chief safety officer at Amazon, stated.
Weak or misconfigured MFA strategies additionally discovered a spot among the many prime 10 most typical community misconfigurations, in line with a brand new joint advisory issued by the U.S. Nationwide Safety Company (NSA) and Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA).
“Some types of MFA are weak to phishing, ‘push bombing,’ exploitation of Signaling System 7 (SS7) protocol vulnerabilities, and/or ‘SIM swap’ methods,” the businesses stated.
“These makes an attempt, if profitable, might permit a risk actor to realize entry to MFA authentication credentials or bypass MFA and entry the MFA-protected techniques.”
The opposite prevalent cybersecurity misconfigurations are as follows –
- Default configurations of software program and functions
- Improper separation of person/administrator privilege
- Inadequate inside community monitoring
- Lack of community segmentation
- Poor patch administration
- Bypass of system entry controls
- Inadequate entry management lists (ACLs) on community shares and providers
- Poor credential hygiene
- Unrestricted code execution
As mitigations, it is beneficial that organizations eradicate default credentials and harden configurations; disable unused providers and implement entry controls; prioritize patching; audit and monitor administrative accounts and privileges.
Software program distributors have additionally been urged to implement safe by design ideas, use memory-safe programming languages the place attainable, keep away from embedding default passwords, present high-quality audit logs to clients at no further cost, and mandate phishing-resistant MFA strategies.
“These misconfigurations illustrate (1) a pattern of systemic weaknesses in lots of giant organizations, together with these with mature cyber postures, and (2) the significance of software program producers embracing secure-by-design ideas to cut back the burden on community defenders,” the businesses famous.