Can particles as tiny as viruses be precisely detected in simply 5 minutes? Scientists from Osaka Metropolitan College assert that it’s certainly attainable by way of their groundbreaking method to ultrafast and extremely delicate quantitative measurement of organic nanoparticles. This innovation holds the potential to revolutionize early illness analysis throughout a large spectrum of sicknesses.
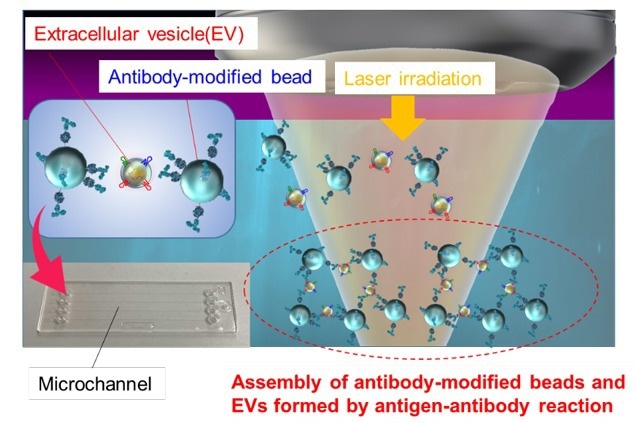
Schematic diagram of light-induced meeting of extracellular vesicles (EV). Utilizing laser irradiation, the researchers managed to straight detect nanoscale EVs in a cell supernatant inside minutes. Picture Credit score: Takuya Iida, Osaka Metropolitan College
Nanoscale extracellular vesicles (EVs), together with exosomes measuring 50–150 nm in diameter, serve essential capabilities in intercellular communication. They’ve additionally gained recognition as biomarkers for varied illnesses and as carriers for drug supply. Therefore, the swift and delicate detection of nanoscale EVs from minute samples is of utmost significance for the early analysis of difficult situations like most cancers and Alzheimer’s illness.
Historically, isolating nanoscale EVs from cell tradition media concerned a fancy and time-consuming process that included ultracentrifugation.
A analysis workforce headed by Director Professor Takuya Iida, Deputy Director Affiliate Professor Shiho Tokonami, and Assistant Director Professor Ikuhiko Nakase on the Analysis Institute for Gentle-induced Acceleration System (RILACS) at Osaka Metropolitan College harnessed the ability of laser mild to expedite the response between nanoscale EVs derived from most cancers cells and microparticles modified with antibodies.
They subsequently examined the three-dimensional construction of the ensuing aggregates utilizing confocal microscopy. Consequently, the researchers efficiently demonstrated the aptitude to detect roughly 103–104 nanoscale EVs current in a 500 nL pattern inside a mere 5-minute timeframe.
This analysis achievement gives a way for ultrafast and ultrasensitive quantitative measurement of organic nanoparticles, providing a basis for progressive evaluation of cell-to-cell communication and early analysis of assorted illnesses sooner or later.
Takuya Iida, Director and Professor, Analysis Institute for Gentle-induced Acceleration System, Osaka Metropolitan College
This examine obtained help from varied sources, together with the JST-Mirai Program (No. JPMJMI18GA, No. JPMJMI21G1), Grant-in-Support for Scientific Analysis (A) (No. JP17H00856, No. JP21H04964), JST FOREST Program (No. JPMJFR201O), Grant-in-Support for Scientific Analysis (B) (No. JP18H03522), Scientific Analysis on Revolutionary Areas (No. JP16H06507), and Grant-in-Support for Early-Profession Scientists (No. JP20K15196) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI. Moreover, the Key Challenge Grant Program of Osaka Prefecture College additionally offered help for this analysis.
Journal Reference
Fujiwara, Okay., et al. (2023). Ultrafast sensitivity-controlled and particular detection of extracellular vesicles utilizing optical power with antibody-modified microparticles in a microflow system. Nanoscale Horizons. doi.org/10.1039/D2NH00576J.
Supply: https://www.omu.ac.jp/en
