Engineering siRNA for enhanced supply is essential, and several other modifications have been developed to enhance siRNA stability, mobile uptake, and intracellular distribution. These modifications might be broadly categorized into two lessons: chemical modifications and formulation-based modifications. Chemical modifications contain altering the molecular construction of siRNA, whereas formulation-based modifications use a supply automobile to encapsulate siRNA or modify its formulation to reinforce supply efficacy [54].
Chemical modification
Chemical modifications have been utilized to enhance the soundness, cut back the immunogenicity, and improve mobile uptake of siRNA molecules. These modifications might be categorized into two teams: nucleotide modifications and phosphate spine modifications [55].
Nucleotide modifications
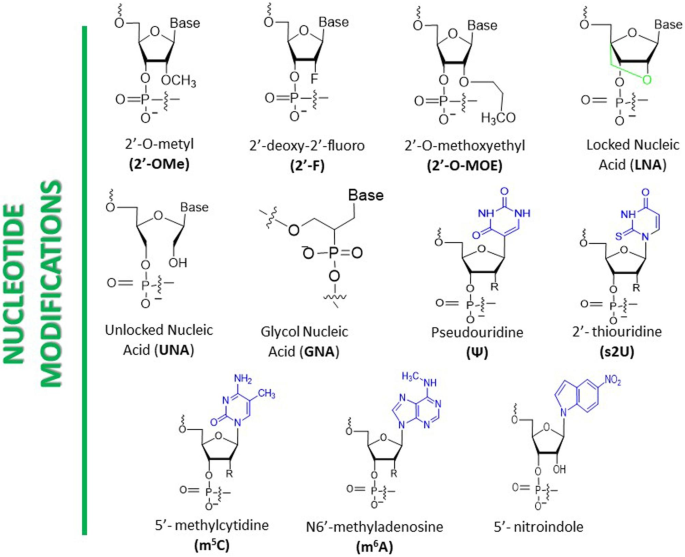
Chemical modifications might be carried out on nucleotide bases, sugar moiety, or nucleosides based mostly on the inherent construction of ribonucleotides. Substituting uridine with 2’-O-methyl uridine (2’-OMe U) is a generally used base modification in siRNA, which has been proven to extend siRNA stability and cut back off-target results (Fig. 3) [56]. One other modification that replaces cytidine with 2’-deoxy-2’-fluoro cytidine (2’-F C) has additionally been discovered to enhance siRNA stability and reduce off-target results [57]. Further base modifications embrace changing adenosine with N6-Methyladenosine (m6 A) [58], guanosine with 2’-O-methyl guanosine (2’-OMe G) [5], and uridine with 2-thiouridine (2-S U) [59]. Sugar modifications regularly employed in siRNA contain substituting ribose with 2’-O-methyl ribose (2’-OMe R) or 2’-fluoro ribose (2’-F R), which have exhibited higher siRNA stability and decreased immunogenicity [60]. Different sugar modifications embrace changing ribose with locked nucleic acid (LNA), unlocked nucleic acid (UNA), glycol nucleic acid (GNA), or 2’-O-methoxyethyl (2’-MOE) sugar [60,61,62]. Essentially the most generally utilized nucleoside modification in siRNA is the incorporation of a 5’-triphosphate cap, which has been proven to reinforce siRNA exercise by facilitating its loading onto the RNA-induced silencing complicated (RISC) [63]. One other nucleoside modification includes attaching a ldl cholesterol moiety to siRNA, bettering its mobile uptake, and selling its accumulation in goal tissues [64].
Phosphate-backbone modification
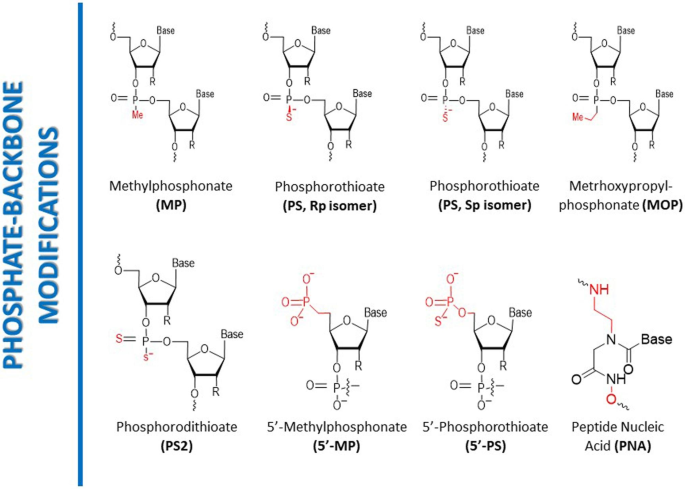
The structural basis of siRNA sometimes consists of phosphodiester bonds, that are weak to breakdown by nucleases [65]. To deal with this situation, phosphonate spine modifications might be employed by substituting the phosphodiester bonds with phosphonate linkages which are proof against nuclease degradation (Fig. 4). One frequent sort of phosphonate spine modification is the addition of a methylphosphonate (MeP) linkage, which replaces one of many non-bridging oxygen atoms of the phosphodiester bond with a methyl group, making a non-ionic and chemically secure linkage [66]. One other modification, phosphorodithioate (PS2) linkage, replaces each non-bridging oxygen atoms of the phosphodiester bond with sulfur atoms, producing a chemically secure and nuclease-resistant linkage. PS2-modified siRNA has demonstrated improved stability and efficacy in comparison with unmodified siRNA and has been efficient in preclinical fashions of most cancers and viral infections [67]. Phosphorothioate (PS) spine modification is one other generally used phosphonate modification. It substitutes the non-bridging oxygen atom of the phosphodiester bond with a sulfur atom, making a negatively charged phosphorothioate linkage. Whereas PS-modified siRNA is extra secure and proof against nuclease degradation than unmodified siRNA, it could trigger off-target results and immune stimulation, limiting its therapeutic potential [68]. Different sorts of phosphonate modifications have additionally been researched, together with phosphoramidate (PA) and phosphoroselenoate (PSe) linkages. The phosphonate spine of siRNA will also be mixed with different modifications, equivalent to sugar modifications, to reinforce the soundness, efficacy, and specificity of siRNA. Integrating MeP or PS2 spine modifications with 2’-O-methyl or 2’-fluoro sugar modifications can confer higher pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic traits upon siRNA, resulting in improved therapeutic outcomes. Moreover, these modifications can cut back off-target results and immune stimulation, bettering the therapeutic potential of siRNA [69, 70].
Formulation-based supply of siRNA therapeutics
To reinforce the efficacy of siRNA, formulation-based modifications can be utilized to guard it from degradation and enhance mobile uptake. Lipid-based formulations, equivalent to liposomes and LNP, are generally utilized resulting from their biocompatibility, ease of formulation, and tissue-targeting skill. These formulations can encapsulate siRNA, defend it from enzymatic degradation, and enhance its mobile uptake via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Polymer-based nanoparticles supply tunable dimension and floor cost for environment friendly mobile uptake and concentrating on, whereas viral vectors equivalent to adeno-associated virus (AAV) and lentivirus have excessive transduction effectivity and the flexibility to combine siRNA into the host genome [71,72,73].
Viral supply methods
The supply of siRNA into goal cells stays a big problem in RNAi expertise. Viral vectors have been developed as efficient methods for delivering siRNA resulting from their skill to contaminate a variety of cell varieties and excessive transduction effectivity. Numerous sorts of viral supply methods have been developed for siRNA, together with adenoviruses, retroviruses, lentiviruses, AAVs, and herpes simplex viruses (HSVs), every with distinctive options and mechanisms appropriate for siRNA supply to particular goal cells [74]. The entry of viral vectors into the goal cells is determined by the kind of vector. As an illustration, adenoviral vectors enter by way of receptor-mediated endocytosis whereas retroviral and lentiviral vectors enter by way of receptor-mediated binding and membrane fusion [24]. Nevertheless, the endosomal pathway poses a big barrier for profitable siRNA supply by viral vectors. To beat these obstacles, viral vectors have developed numerous mechanisms for endosomal escape, together with pH-dependent disruption, fusion with the endosomal membrane, and interplay between the viral capsid and the endosomal membrane. As soon as within the cytoplasm, the viral vector should launch the siRNA to start RNAi, which is determined by the design of the siRNA expression cassette [75,76,77].
Adenoviral vector
Adenoviruses are double-stranded DNA viruses that may infect each people and animals, and they’re generally utilized in gene remedy and vaccination. Adenoviral vectors have been demonstrated to be efficient carriers for siRNA supply since they will transduce a broad vary of cell varieties and carry giant transgene cassettes. Adenoviral vectors enter cells by way of cell floor receptors, and as soon as contained in the cell, the viral DNA is transported to the nucleus the place it’s transcribed and replicated. Nevertheless, one important problem in delivering siRNA by adenoviral vectors is effectively releasing the siRNA from the endosome to the cytoplasm [78]. To beat this impediment, adenoviral vectors have developed numerous methods for endosomal evasion, together with a pH-sensitive method mediated by viral protein VI and induction of auto phagosomes [79, 80]. However, utilizing adenoviral vectors for siRNA supply might trigger toxicity and induce immune responses, which impacts its efficacy [81].
Retroviral vector
Retroviral vectors are generally utilized in gene remedy to offer long-term gene expression by integrating into the host genome. They’re enveloped viruses with a single-stranded RNA genome that bear reverse transcription to kind double-stranded DNA, which then integrates into the host genome. Lately, retroviral vectors have been studied as potential autos for delivering siRNA to downregulate particular gene expression. Retroviral vectors supply benefits equivalent to excessive transduction effectivity and long-term gene expression [82, 83]. Nevertheless, utilizing retroviral vectors for siRNA supply might end in off-target results resulting from their integration into the host genome. To enhance the protection profile of retroviral vectors for siRNA supply, two approaches have been developed. The primary method includes designing self-inactivating (SIN) vectors that comprise a deletion within the U3 area of the lengthy terminal repeat (LTR). This deletion inactivates the promoter and enhancer components within the 3’ LTR, lowering the chance of insertional mutagenesis [84, 85]. The second method includes creating lentiviral vectors, a subclass of retroviral vectors that may transduce non-dividing cells and have a broader host vary. Lentiviral vectors might be pseudo-typed with completely different envelope proteins to focus on particular cell varieties, growing their specificity and lowering off-target results. As well as, lentiviral vectors have a decrease threat of insertional mutagenesis due to their integration desire for energetic genes. These modifications have improved the protection and specificity of retroviral vectors for siRNA supply, making them a promising method for gene remedy purposes [86, 87].
Adeno-associated viral (AAVs) vector
AAV is a promising viral vector for gene remedy and RNAi purposes resulting from its low immunogenicity, skill to transduce each dividing and non-dividing cells, and long-term gene expression [88]. AAV-mediated siRNA supply includes utilizing recombinant AAV vectors that carry a therapeutic siRNA cassette underneath the management of a tissue-specific promoter to silence goal genes. The AAV vector is produced by co-transfecting a packaging cell line with the AAV vector plasmid and a helper plasmid that gives the lacking viral genes in trans., adopted by purification from the cell lysate [89, 90]. Regardless of its benefits, AAV-mediated siRNA supply encounters hurdles equivalent to restricted packaging capability, off-target results, and lack of efficacy in particular cell varieties [91]. To deal with these obstacles, numerous approaches have been developed, together with introducing mutations into AAV vectors to reinforce transduction effectivity and cut back immunogenicity and using self-complementary AAV (scAAV) for siRNAs to extend efficiency [92]. Nevertheless, regardless of these challenges, the advantages of AAV-mediated siRNA supply outweigh the drawbacks. The low immunogenicity of AAV permits for repeated dosing, whereas its skill to transduce each dividing and non-dividing cells makes it an appropriate vector for siRNA supply to post-mitotic tissues equivalent to neurons and muscle cells. Moreover, AAV can obtain long-term gene expression within the goal tissue, making it a promising software for gene remedy and RNAi purposes [89, 93, 94].
AAV has potential purposes in siRNA remedy for a variety of ailments, together with viral infections, genetic issues, most cancers, and neurodegenerative ailments. By modifying AAVs to specific siRNA molecules that concentrate on particular genes, AAV-delivered siRNAs can forestall viral replication, cut back the manufacturing of disease-causing proteins, inhibit tumor development, and gradual or reverse illness development. These approaches have been explored in research and have proven promising leads to preclinical and medical settings, demonstrating the potential of AAV-based siRNA therapies for treating numerous ailments [93, 95, 96].
Herpes simplex viruses (HSVs) vector
HSVs are a cluster of viral particles that may trigger numerous infections, starting from chilly sores to genital herpes. HSVs have the flexibility to ascertain a latent an infection within the host, which might later set off recurrent outbreaks. This attribute has piqued the curiosity of researchers who’re investigating their potential as vectors for delivering therapeutic brokers, equivalent to siRNAs. HSVs are appropriate candidates for siRNA supply resulting from their capability to contaminate a variety of cell varieties and set up persistent latent infections [97, 98]. As well as, HSVs have a big genome that may accommodate overseas DNA sequences, making them an optimum platform for gene supply. By engineering HSVs to specific siRNAs that selectively goal viral genes, viral replication and transmission might be inhibited. HSVs will also be designed to focus on particular cell varieties, enabling focused supply of siRNAs to contaminated cells [97, 99].
Quite a few research have explored the usage of HSVs as siRNA carriers for treating viral infections, together with these brought on by HSV-1 and HSV-2 [100]. HSVs naturally goal most cancers cells and may invade and reproduce selectively in tumor cells whereas preserving regular cells. Moreover, HSVs might be genetically modified to specific therapeutic genes or siRNAs that particularly goal most cancers cells, inflicting tumor cell loss of life. A number of research have confirmed the potential of HSVs as siRNA carriers for treating numerous cancers, equivalent to breast most cancers, melanoma, and glioblastoma [101, 102].
Nevertheless, HSV-based siRNA supply methods have limitations and challenges. One important concern is the potential for the virus reactivating and inflicting illness within the host, regardless of establishing long-term latent infections. This may end up in repeated herpes outbreaks [103]. As well as, the host immune response might impair the efficacy of the virus as a gene remedy vector. The immune system can establish and clear the virus, proscribing its skill to move siRNAs to focus on cells [102].
Non-viral supply methods
Though viral vectors have been proven to successfully ship siRNA and have the potential to remedy quite a few ailments, there’s a want for various supply methods that may overcome present limitations and enhance efficacy. Non-viral supply methods for siRNA have emerged as a promising various by providing a safer and extra environment friendly method to delivering siRNA to focus on cells. These methods make the most of numerous nanoparticle-based methods, together with lipid-based, cell-penetrating peptides, polymeric, and inorganic supply methods [104]. Lipid-based supply methods, equivalent to liposomes and strong lipid nanoparticles, can encapsulate siRNA in a protecting lipid bilayer, enhancing their stability and mobile internalization [105]. Polymeric supply methods, equivalent to polyethyleneimine and chitosan, might be designed to ship siRNA particularly to sure cell varieties [106]. Inorganic supply methods, equivalent to gold and silica nanoparticles, might be engineered to functionalize siRNA with concentrating on ligands for exact supply [72]. Non-viral supply methods have exhibited important potential in delivering siRNA to a variety of cell varieties in vitro and in vivo, together with most cancers and immune cells. Nevertheless, the efficacy of those methods might be additional enhanced by addressing points associated to toxicity and immune response [22].
Lipid-based supply methods
Lipid-based supply methods supply an efficient method for delivering siRNA by encapsulating it inside a protecting lipid bilayer, which reinforces its stability and protects it from degradation (Desk 1; Fig. 5). Lipid-based nanoparticles, equivalent to liposomes and strong lipid nanoparticles, are generally used as carriers for siRNA supply resulting from their biocompatibility, low toxicity, and capability to move each hydrophilic and hydrophobic siRNA molecules [105]. The lipid bilayer will also be functionalized with ligands to enhance concentrating on and uptake of particular cells or tissues. Lipid-based supply methods have benefits over different supply methods, equivalent to viral vectors, together with decrease immunogenicity, bigger cargo capability, and simpler synthesis and modification [107].
Latest advances in lipid-based supply methods for siRNA goal to reinforce the specificity, stability, and effectivity of siRNA supply to focus on cells. Hybrid lipid-based nanoparticles that mix completely different lipid formulations have been created, equivalent to a cationic and fusogenic lipid hybrid nanoparticle that confirmed superior gene silencing efficacy and decreased toxicity in most cancers cells. Stimuli-responsive lipids have been used to develop pH-sensitive lipid nanoparticles that selectively launch siRNA within the acidic setting of tumor cells, enhancing gene silencing [112]. Focusing on ligands have additionally been integrated into lipid-based nanoparticles to enhance the specificity of siRNA supply, resulting in enhanced gene silencing and inhibition of tumor development [113]. Moreover, lyophilization has been used to enhance the soundness of lipid-based nanoparticles throughout storage and circulation within the bloodstream. As an illustration, a lyophilized lipid nanoparticle for delivering siRNA concentrating on most cancers cells exhibited excessive stability and preserved gene silencing efficacy after reconstitution. These latest approaches maintain nice promise for creating efficient siRNA therapeutics [114, 115].
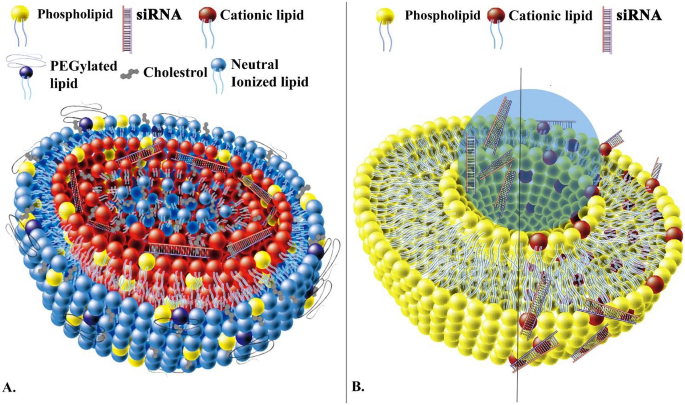
LNPs for siRNA supply. (A) siRNA-encapsulated in core of LNPs. (B) liposome-mediated supply of siRNA. Liposomes’ inside water part encapsulates siRNA or siRNA binds to cationic lipid-containing liposomes. [105]
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs)
CPPs are a gaggle of quick peptides that may transport numerous biomolecules, together with peptides, proteins, nucleic acids, and nanoparticles, throughout mobile membranes by penetrating the cell membrane [116]. The invention of CPPs dates again to 1988 when arginine-rich peptides had been recognized within the HIV-1 Tat protein that facilitated its entry into cells and translocation to the nucleus [117]. A number of CPPs have been recognized, equivalent to cationic peptides, which comprise a excessive proportion of positively charged amino acids, and amphipathic peptides, which possess each hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids. Amphipathic peptides work together with the lipid bilayer to facilitate mobile uptake [118].
CPPs can transport siRNA throughout the cell membrane however lack specificity and could also be taken up by non-target cells, lowering their effectiveness and inflicting toxicity [116, 119]. To extend specificity for goal cells, CPPs might be conjugated with concentrating on ligands, equivalent to antibodies or peptides (Fig. 6). This method has been demonstrated in utilizing an anti-EGFR antibody as a concentrating on ligand with CPP appearing as an environment friendly facilitator of mobile uptake, leading to particular supply of siRNA to EGFR-positive most cancers cells with out impacting the viability or operate of non-cancerous cells [120].
One other technique is the usage of CPPs modified with a pH-sensitive moiety that permits for selective launch of the siRNA payload within the acidic tumor microenvironment, resulting in enhanced gene silencing and inhibition of tumor development [121]. Self-assembling peptides (SAPs) have additionally been utilized for siRNA encapsulation and safety to enhance stability and pharmacokinetics [122, 123]. The usage of multivalent SAPs, which comprise a number of copies of the siRNA-binding motif, will increase the affinity and specificity for siRNA, leading to larger transfection effectivity and decreased off-target results [124, 125]. SAPs will also be modified with concentrating on ligands that solely bind to receptors positioned on the floor of goal cells or tissues, bettering siRNA transport to tumor cells and the effectiveness of the remedy [126].
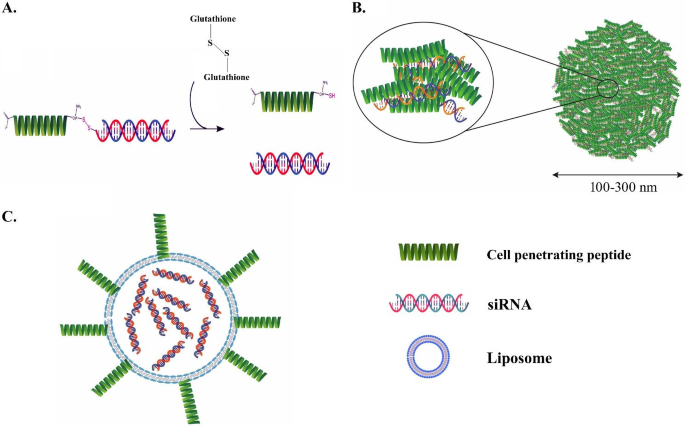
CPPs for siRNA supply. (A) Covalently conjugated siRNA with CPP. (B) siRNA complexed with the CPP and (C) CPP-decorated nanoparticle. [116]
Meade et al. developed a self-delivering siRNA platform composed of impartial phosphotriesters as internucleotide linkages that may be transformed to negatively charged siRNA by way of cytoplasmic thioesterase. They conjugated hydrazine-containing peptide domains to siRNAs with aldehyde phosphotriester teams, which circumvented the lack of CPP exercise noticed in earlier research. In vitro experiments confirmed that these multi-Tat-siRNA conjugates successfully inhibited goal protein expressions with out the necessity for a transfection reagent. Growing the variety of multi-Tat peptide domains within the siRNA construction improved goal protein silencing. Nevertheless, this siRNA-peptide conjugate has not been utilized in vivo [127].
Aptamers
Aptamer-mediated siRNA supply is a promising method for focused supply of siRNA molecules into cells. Aptamers are quick, single-stranded nucleic acid molecules that possess excessive specificity and affinity for particular goal molecules. By combining aptamers with siRNA, it’s doable to attain focused supply into cells, inducing gene silencing and therapeutic results [128]. In comparison with conventional supply strategies, aptamer-mediated siRNA supply affords the benefits of particular cell and tissue concentrating on in addition to sustained gene silencing, which can lower the necessity for frequent dosing [129]. Aptamers have been designed to particularly goal immune cells [130], cell floor receptors [129], and inflammatory markers [131] for siRNA supply. The design of aptamers is crucial for efficacy and specificity, and numerous approaches have been devised to enhance aptamer-mediated siRNA supply. These embrace multifunctional aptamer-siRNA conjugates [132] and stimuli-responsive aptamers [133]. Nevertheless, creating aptamers with excessive specificity and affinity for his or her goal molecules stays difficult.
Deciding on aptamers that bind particularly to focus on cells or tissues is an important step in creating an aptamer-mediated siRNA supply system. Latest developments in aptamer choice applied sciences, equivalent to SELEX and high-throughput sequencing, have enabled the identification of aptamers with excessive affinity and specificity to varied targets. Aptamer modification methods, equivalent to chemical modifications (e.g., LNAs or 2’-fluoropyrimidine modifications) and the addition of PEG moieties, have been explored to enhance their binding affinity and specificity [132, 135]. Furthermore, numerous conjugation methods have been launched, together with thiol-modified aptamers and covalent linkages (e.g., click on chemistry or amidation), to attain secure and environment friendly siRNA conjugation to aptamers [136, 137].
Focusing on is one other facet of aptamer-mediated siRNA supply. The identification of concentrating on aptamers might be achieved via SELEX, which permits screening of oligonucleotide libraries for aptamers with excessive binding affinity to particular cells or tissues. Lately, the sphere has made important progress in enhancing the specificity and selectivity of aptamer-siRNA conjugates via novel concentrating on methods [138]. One such method includes the usage of a number of aptamers to focus on distinct receptors on the identical cell or tissue, thereby lowering the chance of off-target results and bettering specificity. An instance is the aptamer-siRNA conjugate designed to focus on each EGFR and HER2 in breast most cancers cells, which demonstrated enhanced selectivity and efficacy [138, 139]. One other technique entails concentrating on tumor-associated antigens (TAAs), proteins which are overexpressed on the floor of most cancers cells however absent on regular cells, using aptamers that concentrate on TAAs can considerably improve the specificity of the conjugate and cut back off-target results. The aptamer-siRNA conjugate designed to focus on PSMA in prostate most cancers cells has exhibited favorable outcomes in augmenting each selectivity and effectiveness [134].
Polymeric nanoparticles
Polymeric nano-carriers designed for focused supply of siRNA to particular cells supply a promising and progressive method to beat the challenges related to conventional siRNA supply strategies, equivalent to poor mobile uptake, low stability, and non-specific distribution all through the physique. The usage of polymeric nanoparticles composed of biocompatible and biodegradable polymers, together with PLGA, PEG, PLL, chitosan, and polyethyleneimine (PEI) presents a possible avenue for enhanced effectiveness and specificity of siRNA supply, with minimized off-target results, resulting in safer and simpler remedies for numerous issues. These nanoparticles might be engineered to encapsulate and shield siRNA from degradation, improve mobile uptake, and permit managed launch of siRNA on the goal web site. Focusing on ligands, equivalent to peptides or antibodies, will also be integrated into polymeric nanoparticles to reinforce specificity and selectivity [106, 140,141,142].
Lately, substantial progress has been made within the discipline of polymeric nanoparticles for siRNA supply. New cationic polymers, equivalent to PAMAM, PBAE, and PEI, have been developed and chemically modified to enhance their effectivity and cut back their toxicity (Desk 2). As an illustration, PAMAM has been modified with hydrophobic teams to enhance its stability in serum, leading to a possible enhance in in vitro transfection effectivity of PAMAM-based siRNA supply vectors [143]. Equally, PBAE has been modified with oligopeptide linkages to lower its toxicity whereas sustaining transfection effectivity. Modified PBAE polymers have proven environment friendly and low toxicity siRNA supply to varied cell varieties [144]. Whereas PEI is extensively used for siRNA supply, owing to its distinctive attributes. PEI employs its larger cost density to ascertain robust electrostatic interplay with negatively charged siRNA molecules, offering environment friendly extracellular degradation safety. Of explicit significance, PEI’s skill to manage endosomal escape, a capability usually ascribed to the well-documented “proton sponge impact”. Moreover, PEI’s structural versatility, which incorporates the flexibility to fine-tune molecular weight, introduce branching modifications, and execute functionalization, makes it well-suited for the difference of supply methods, addressing explicit wants within the siRNA supply area. Nevertheless, important challenges emerge inside this rising discipline, most notably the difficulty of cytotoxicity related to excessive molecular weight PEI, which has prompted in depth analysis into various PEI variants engineered to restrict toxicity, providing promising prospects for safer siRNA supply approaches [145]. Modified PEI polymers have been developed with improved efficacy and decreased toxicity, equivalent to PEGylation of PEI to cut back toxicity whereas preserving its siRNA supply capability [146]. As well as, hybrid nanoparticles composed of each cationic polymers and lipids have been developed, bettering stability, specificity, and efficacy of siRNA supply [147].
One other important development is the event of bioreducible polymers that may bear degradation or breakdown in response to particular intracellular stimuli, equivalent to lowering brokers or reactive oxygen species. This results in the discharge of siRNA into the cytoplasm of goal cells, enhancing the specificity of siRNA supply [148]. Bioreducible polymers have exhibited proficient siRNA supply for anti-inflammatory remedy in opposition to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion harm, together with disulfide-containing branched poly(?-amino ester) (SS-b-PAE) polymer for delivering siRNA to microvascular endothelial cells, which promoted therapeutic efficacy and decreased post-transfection toxicity [149]. Likewise, thiolated chitosan polymer was discovered to be biocompatible and efficient in delivering siRNA to breast most cancers cells in vitro and in vivo [150].
Furthermore, core-shell hybrid nanoparticles have been synthesized utilizing block copolymers, together with PEG-b-PLA and PEG-b-PLGA, usually mixed with cationic lipids to encapsulate and launch siRNA. As an illustration, Yang et al. employed PEG-b-PLA/BHEM-Chol nanoparticles to downregulate polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) and suppress tumor development in mice fashions [156, 157]. Furthermore, PLGA-based block copolymer methods have been devised by Farokhzad and colleagues for systemic supply of siRNA in opposition to a wide range of targets, exhibiting effectiveness in a prostate most cancers mannequin [158].