To gauge the pondering of enterprise decision-makers at this crossroads, MIT Expertise Evaluation Insights polled 1,000 executives about their present and anticipated generative AI use instances, implementation obstacles, know-how methods, and workforce planning. Mixed with insights from an knowledgeable interview panel, this ballot affords a view into as we speak’s main strategic issues for generative AI, serving to executives motive by way of the most important selections they’re being known as upon to make.
Key findings from the ballot and interviews embrace the next:
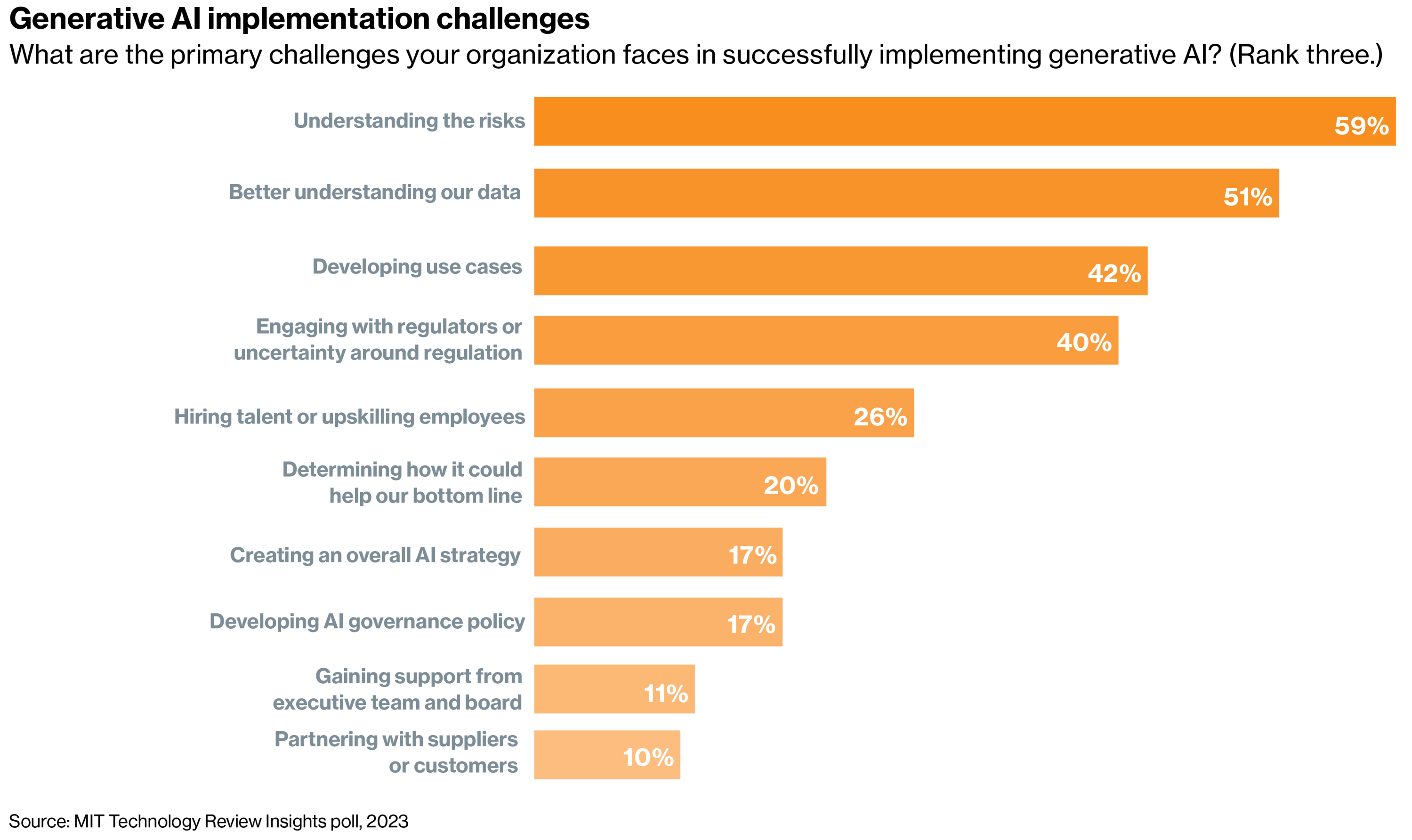
- Executives acknowledge the transformational potential of generative AI, however they’re transferring cautiously to deploy. Almost all companies imagine generative AI will have an effect on their enterprise, with a mere 4% saying it is not going to have an effect on them. However at this level, solely 9% have absolutely deployed a generative AI use case of their group. This determine is as little as 2% within the authorities sector, whereas monetary providers (17%) and IT (28%) are the most certainly to have deployed a use case. The largest hurdle to deployment is knowing generative AI dangers, chosen as a top-three problem by 59% of respondents.
- Firms is not going to go it alone: Partnerships with each startups and Massive Tech will probably be essential to clean scaling. Most executives (75%) plan to work with companions to deliver generative AI to their group at scale, and only a few (10%) think about partnering to be a high implementation problem, suggesting {that a} sturdy ecosystem of suppliers and providers is obtainable for collaboration and co-creation. Whereas Massive Tech, as builders of generative AI fashions and purveyors of AI-enabled software program, has an ecosystem benefit, startups take pleasure in benefits in a number of specialised niches. Executives are considerably extra more likely to plan to staff up with small AI-focused firms (43%) than giant tech companies (32%).
- Entry to generative AI will probably be democratized throughout the economic system. Firm measurement has no bearing on a agency’s chance to be experimenting with generative AI, our ballot discovered. Small firms (these with annual income lower than $500 million) had been thrice extra seemingly than mid-sized companies ($500 million to $1 billion) to have already deployed a generative AI use case (13% versus 4%). In reality, these small firms had deployment and experimentation charges just like these of the very largest firms (these with income higher than $10 billion). Inexpensive generative AI instruments may increase smaller companies in the identical manner as cloud computing, which granted firms entry to instruments and computational sources that will as soon as have required large monetary investments in {hardware} and technical experience.

- One-quarter of respondents count on generative AI’s major impact to be a discount of their workforce. The determine was larger in industrial sectors like vitality and utilities (43%), manufacturing (34%), and transport and logistics (31%). It was lowest in IT and telecommunications (7%). Total, this can be a modest determine in comparison with the extra dystopian job alternative eventualities in circulation. Demand for abilities is rising in technical fields that target operationalizing AI fashions and in organizational and administration positions tackling thorny subjects together with ethics and danger. AI is democratizing technical abilities throughout the workforce in ways in which may result in new job alternatives and elevated worker satisfaction. However consultants warning that, if deployed poorly and with out significant session, generative AI may degrade the qualitative expertise of human work.
- Regulation looms, however uncertainty is as we speak’s biggest problem. Generative AI has spurred a flurry of exercise as legislators attempt to get their arms across the dangers, however really impactful regulation will transfer on the pace of presidency. Within the meantime, many enterprise leaders (40%) think about participating with regulation or regulatory uncertainty a major problem of generative AI adoption. This varies vastly by business, from a excessive of 54% in authorities to a low of 20% in IT and telecommunications.
This content material was produced by Insights, the customized content material arm of MIT Expertise Evaluation. It was not written by MIT Expertise Evaluation’s editorial employees.

