Rats are extremely nimble creatures. They will climb up curtains, leap down tall ledges, and scurry throughout advanced terrain—say, your basement stacked with odd-shaped stuff—at mind-blowing velocity.
Robots, in distinction, are something however nimble. Regardless of current advances in AI to information their actions, robots stay stiff and clumsy, particularly when navigating new environments.
To make robots extra agile, why not management them with algorithms distilled from organic brains? Our actions are rooted within the bodily world and primarily based on expertise—two parts that permit us simply discover completely different environment.
There’s one main impediment. Regardless of a long time of analysis, neuroscientists haven’t but pinpointed how mind circuits management and coordinate motion. Most research have correlated neural exercise with measurable motor responses—say, a twitch of a hand or the velocity of lifting a leg. In different phrases, we all know mind activation patterns that may describe a motion. However which neural circuits trigger these actions within the first place?
We might discover the reply by attempting to recreate them in digital type. Because the well-known physicist Richard Feynman as soon as mentioned, “What I can not create, I don’t perceive.”
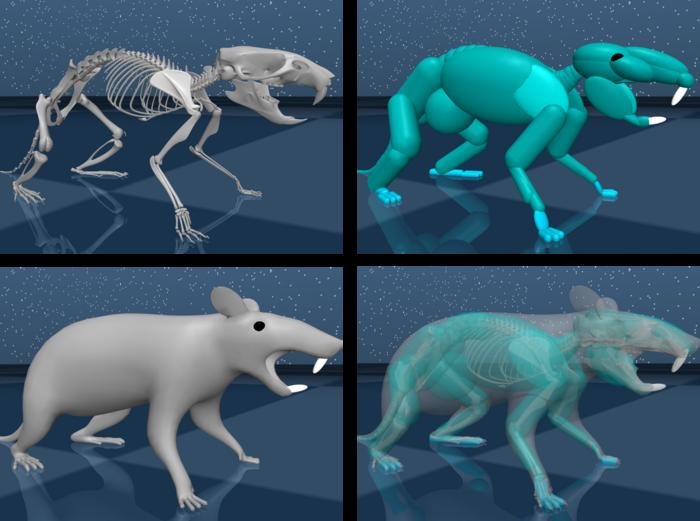
This month, Google DeepMind and Harvard College constructed a sensible digital rat to dwelling in on the neural circuits that management advanced motion. The rat’s digital mind, composed of synthetic neural networks, was skilled on tens of hours of neural recordings from precise rats operating round in an open area.
Evaluating activation patterns of the unreal mind to indicators from residing, respiratory animals, the group discovered the digital mind might predict the neural activation patterns of actual rats and produce the identical habits—for instance, operating or rearing up on hind legs.
The collaboration was “implausible,” mentioned examine writer Dr. Bence Ölveczky at Harvard in a press launch. “DeepMind had developed a pipeline to coach biomechanical brokers to maneuver round advanced environments. We merely didn’t have the sources to run simulations like these, to coach these networks.”
The digital rat’s mind recapitulated two areas particularly vital for motion. Tweaking connections in these areas modified motor responses throughout a wide range of behaviors, suggesting these neural indicators are concerned in strolling, operating, climbing, and different actions.
“Digital animals skilled to behave like their actual counterparts might present a platform for digital neuroscience…that might in any other case be troublesome or unattainable to experimentally deduce,” the group wrote of their article.
A Dense Dataset
Synthetic intelligence “lives” within the digital world. To energy robots, it must perceive the bodily world.
One strategy to train it in regards to the world is to file neural indicators from rodents and use the recordings to engineer algorithms that may management biomechanically lifelike fashions replicating pure behaviors. The objective is to distill the mind’s computations into algorithms that may pilot robots and likewise give neuroscientists a deeper understanding of the mind’s workings.
Up to now, the technique has been efficiently used to decipher the mind’s computations for imaginative and prescient, scent, navigation, and recognizing faces, the authors defined of their paper. Nevertheless, modeling motion has been a problem. People transfer in another way, and noise from mind recordings can simply mess up the ensuing AI’s precision.
This examine tackled the challenges head on with a cornucopia of information.
The group first positioned a number of rats right into a six-camera area to seize their motion—operating round, rearing up, or spinning in circles. Rats might be lazy bums. To encourage them to maneuver, the group dangled Cheerios throughout the sector.
Because the rats explored the sector, the group recorded 607 hours of video and likewise neural exercise with a 128-channel array of electrodes implanted of their brains.
They used this knowledge to coach a man-made neural community—a digital rat’s “mind”—to regulate physique motion. To do that, they first tracked how 23 joints moved within the movies and transferred them to a simulation of the rats’ skeletal actions. Our joints solely bend in sure methods, and this step filters out what’s bodily unattainable (say, bending legs in the other way).
The core of the digital rat’s mind is a kind of AI algorithm referred to as an inverse dynamics mannequin. Mainly, it is aware of the place “physique” positions are in house at any given time and, from there, predicts the subsequent actions resulting in a objective—say, seize that espresso cup with out dropping it.
By way of trial-and-error, the AI ultimately got here near matching the actions of its organic counterparts. Surprisingly, the digital rat might additionally simply generalize motor abilities to unfamiliar locations and situations—partly by studying the forces wanted to navigate the brand new environments.
The similarities allowed the group to match actual rats to their digital doppelgangers, when performing the identical habits.
In a single take a look at, the group analyzed exercise in two mind areas recognized to information motor abilities. In comparison with an older computational mannequin used to decode mind networks, the AI might higher simulate neural indicators within the digital rat throughout a number of bodily duties.
Due to this, the digital rat gives a strategy to examine motion digitally.
One long-standing query, for instance, is how the mind and nerves command muscle motion relying on the duty. Grabbing a cup of espresso within the morning, for instance, requires a gentle hand with none jerking motion however sufficient energy to carry it regular.
The group tweaked the “neural connections” within the digital rodent to see how adjustments in mind networks alter the ultimate habits—getting that cup of espresso. They discovered one community measure that might determine a habits at any given time and information it via.
In comparison with lab research, these insights “can solely be instantly accessed via simulation,” wrote the group.
The digital rat bridges AI and neuroscience. The AI fashions right here recreate the physicality and neural indicators of residing creatures, making them invaluable for probing mind capabilities. On this examine, one facet of the digital rat’s motor abilities relied on two mind areas—pinpointing them as potential areas key to guiding advanced, adaptable motion.
The same technique might present extra perception into the computations underlying imaginative and prescient, sensation, or maybe even increased cognitive capabilities akin to reasoning. However the digital rat mind isn’t an entire replication of an actual one. It solely captures snapshots of a part of the mind. However it does let neuroscientists “zoom in” on their favourite mind area and take a look at hypotheses rapidly and simply in comparison with conventional lab experiments, which frequently take weeks to months.
On the robotics facet, the strategy provides a physicality to AI.
“We’ve discovered an enormous quantity from the problem of constructing embodied brokers: AI methods that not solely need to suppose intelligently, but additionally need to translate that pondering into bodily motion in a fancy setting,” mentioned examine writer Dr. Matthew Botvinick at DeepMind in a press launch. “It appeared believable that taking this identical strategy in a neuroscience context could be helpful for offering insights in each habits and mind operate.”
The group is subsequent planning to check the digital rat with extra advanced duties, alongside its organic counterparts, to additional peek contained in the interior workings of the digital mind.
“From our experiments, we’ve got numerous concepts about how such duties are solved,” mentioned Ölveczky to The Harvard Gazette. “We need to begin utilizing the digital rats to check these concepts and assist advance our understanding of how actual brains generate advanced habits.”
Picture Credit score: Google DeepMind