Age catches up with us all. Eyes wrestle to focus. Muscle tissues wither away. Reminiscence dwindles. The danger of hypertension, diabetes, and different age-related ailments skyrockets.
A myriad of anti-aging therapies are within the works, and a brand new one simply joined the fray. In mice, blocking a protein that promotes irritation in center age elevated metabolism, lowered muscle losing and frailty, and diminished the probabilities of most cancers.
Not like most earlier longevity research that tracked the well being of getting old male mice, the research concerned each sexes, and the remedy labored throughout the board.
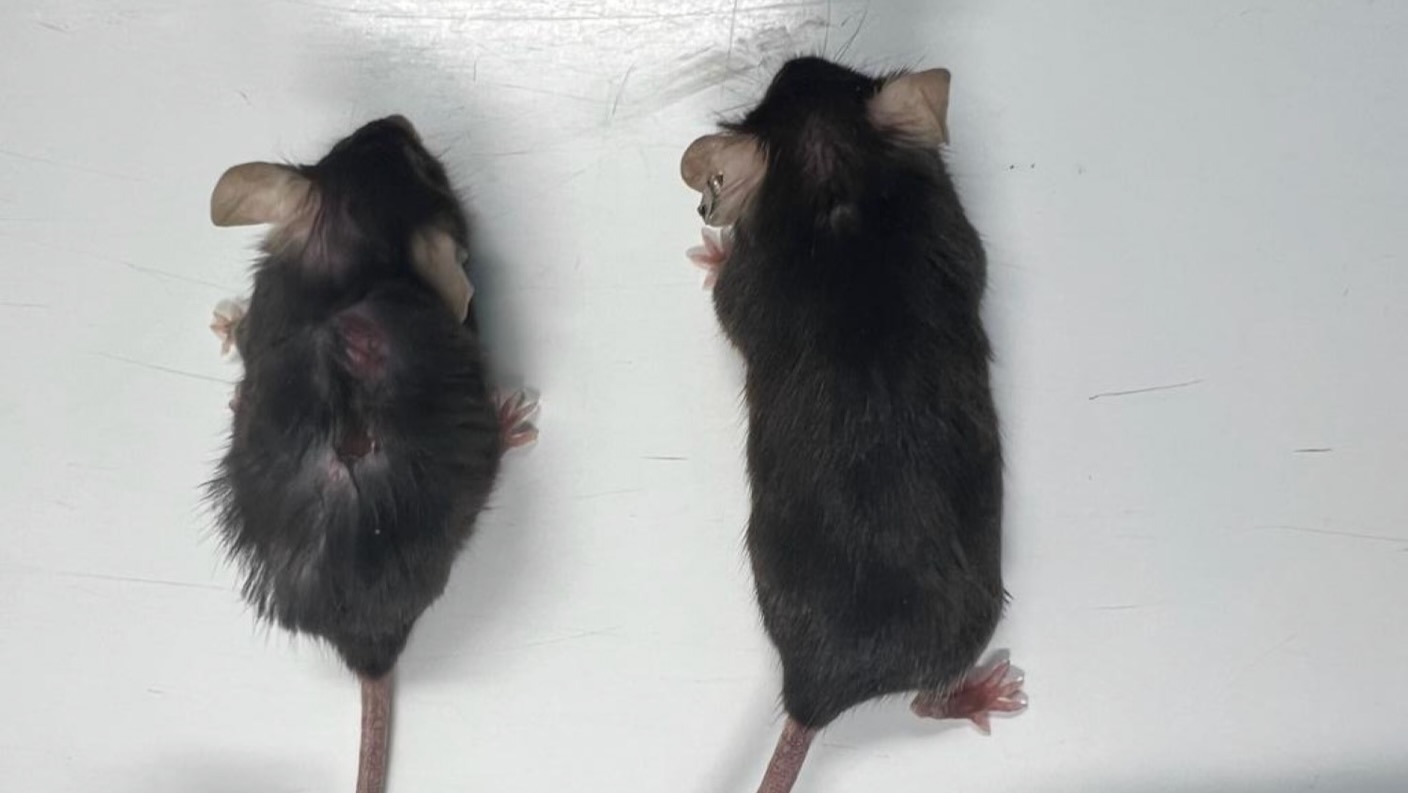
Lovingly known as “supermodel grannies” by the group, the aged woman mice seemed and behaved far youthful than their age, with shiny coats of fur, much less fatty tissue, and muscular tissues rivaling these of a lot youthful mice.
The therapy didn’t simply enhance wholesome longevity, also called healthspan—the variety of years dwelling with out ailments—it additionally elevated the mice’s lifespan by up 25 %. The common life expectancy of individuals within the US is roughly 77.5 years. If the outcomes translate from mice to folks—and that’s a really large if—it might imply a bump to nearly 97 years.
The protein, dubbed IL-11, has been in scientists’ crosshairs for many years. It promotes irritation and causes lung and kidney scarring. It’s additionally been related to numerous sorts of cancers and senescence. The probability of all these situations will increase as we age.
Amongst a slew of pro-aging proteins already found, IL-11 stands out because it might make a beeline for testing in people. Blockers for IL-11 are already within the works for treating most cancers and tissue scarring. Though medical trials are nonetheless ongoing, early outcomes present the medicine are comparatively protected in people.
“Beforehand proposed life-extending medicine and coverings have both had poor side-effect profiles, or don’t work in each sexes, or might prolong life, however not wholesome life, nonetheless this doesn’t seem like the case for IL-11,” mentioned research writer Dr. Stuart Cook dinner in a press launch. “These findings are very thrilling.”
Unusual Coincidence
In 2017, Cook dinner zeroed in on IL-11 as a therapy goal for coronary heart and kidney scarring, not longevity. Injecting IL-11 triggered the situations, finally resulting in organ failure. Genetically deleting the protein protected towards the ailments.
It’s straightforward to name IL-11 a villain. However the protein is a necessary a part of the immune system. Produced by the bone marrow, it’s essential for embryo implantation. It additionally helps sure sorts of blood cells develop and mature, notably people who cease bleeding after a scrape.
With age, nonetheless, the protein tends to goes rogue. It sparks irritation throughout the physique, damaging cells and tissues and contributing to most cancers, autoimmune problems, and tissue scarring. A “hallmark of getting old,” irritation has lengthy been focused as a strategy to scale back age-related ailments. Though IL-11 is a identified set off for irritation, it hasn’t been instantly linked to getting old.
Till now. The story is one among probability.
“This venture began again in 2017 when a collaborator of ours despatched us some tissue samples for an additional venture,” mentioned research writer Anissa Widjaja within the press launch. She was testing a way to precisely detect IL-11. A number of samples of an outdated rat’s proteins had been within the combine, and he or she realized that IL-11 ranges had been far greater within the samples than in these from youthful mice.
“From the readings, we might clearly see that the degrees of IL-11 elevated with age, and that’s after we bought actually excited,” she mentioned.
Longevity Blocker
The outcomes spurred the group to shift their analysis focus to longevity. A collection of assessments confirmed IL-11 ranges constantly rose in a wide range of tissues—muscle, fats, and liver—in each female and male mice as they aged.
To see how IL-11 influences the physique, the group subsequent deleted the gene coding for IL-11 and in contrast mice with out the protein to their regular friends. At two years outdated, thought-about aged for mice, tissues in regular people had been plagued by genetic signatures suggesting senescence—when cells lose their operate however are nonetheless alive. Usually known as “zombie cells,” they spew out a poisonous mixture of inflammatory molecules and hurt their neighbors. Aged mice with out IL-11, nonetheless, had senescence genetic profiles much like these of a lot youthful mice.
Deleting IL-11 had different perks. Weight achieve is frequent with age, however with out IL-11, the mice maintained their slim form and had decrease ranges of fats, better lean muscle mass, and glossy, full coats of fur. It’s not nearly seems to be. Levels of cholesterol and markers for liver harm had been far decrease than in regular friends. Aged mice with out IL-11 had been additionally spared shaking tremors—in any other case frequent in aged mice—and will flexibly regulate their metabolism relying on the amount of meals they ate.
The advantages additionally confirmed up of their genetic materials. DNA is protected by telomeres—a form of finish cap on chromosomes—that dwindle in size with age. Ridding cells of IL-11 prevented telomeres from eroding away within the livers and muscular tissues of the aged mice.
Genetically deleting IL-11 is a stretch for medical use in people. The group subsequent turned to a extra possible different: An antibody shot. Antibodies can seize onto a goal, on this case IL-11, and forestall it from functioning.
Starting at 75 weeks, roughly the equal of 55 human years, the mice acquired an antibody shot each month for 25 weeks—over half a 12 months. Related antibodies are already being examined in medical trials.
The well being advantages in these mice matched these in mice with out IL-11. Their weight and fats decreased, they usually might higher deal with sugar. In addition they fought off indicators of frailty as they aged, experiencing minimal tremors and issues with gait and sustaining greater metabolisms. Quite than losing away, their muscular tissues had been even stronger than in the beginning of the research.
The therapy didn’t simply enhance healthspan. Month-to-month injections of the IL-11 antibody till pure dying additionally elevated lifespan in each female and male mice by as much as 25 %.
“These findings are very thrilling. The handled mice had fewer cancers and had been free from the standard indicators of getting old and frailty… In different phrases, the outdated mice receiving anti-IL-11 had been more healthy,” mentioned Cook dinner.
Though IL-11 antibody medicine are already in medical trials, translating these outcomes to people might face hurdles. Mice have a comparatively quick lifespan. A long life trial in people can be lengthy and really costly. The handled mice had been additionally contained in a lab setting, whereas in the actual world we roam round and have differing existence—weight loss program, train, ingesting, smoking—that would confound outcomes. Even when it really works in people, a shot each month starting in center age would possible rack up a hefty invoice, offering well being and life extension solely to those that might afford it.
To Cook dinner, somewhat than specializing in extending longevity per se, tackling a particular age-related drawback, akin to tissue scarring or dropping muscular tissues is a greater different for now.
“Whereas these findings are solely in mice, it raises the tantalizing chance that the medicine might have an identical impact in aged people. Anti-IL-11 therapies are presently in human medical trials for different situations, doubtlessly offering thrilling alternatives to review its results in getting old people sooner or later,” he mentioned.
Picture Credit score: MRC LMS, Duke-NUS Medical Faculty