From deep-earth exploration to the depths of house, uncover how this sturdy know-how may energy the way forward for AI and past.

When smartphones shut down throughout a seaside day, it’s sometimes because of their digital parts failing to face up to the warmth. This failure happens as a result of the reminiscence chips aren’t designed to deal with excessive temperatures, inflicting knowledge loss as electrons destabilise and escape. Addressing this problem, researchers on the College of Pennsylvania’s Faculty of Engineering and Utilized Science have made a big breakthrough.
Their groups developed a reminiscence know-how that endures temperatures as much as 600° Celsius (1112° Fahrenheit). This temperature is greater than double the brink of business reminiscence drives. Impressively, their gadget maintained stability for over 60 hours, suggesting a brand new benchmark in sturdiness.
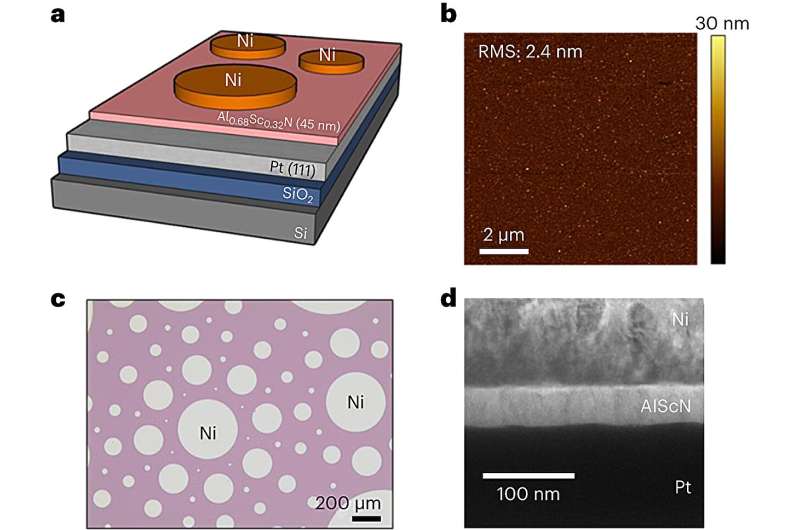
The brand new reminiscence gadget makes use of ferroelectric aluminum scandium nitride (AlScN). In contrast to conventional silicon-based recollections, which fail round 200° Celsius (392° Fahrenheit), AlScN can retain knowledge at a lot increased temperatures. It operates on a metal-insulator-metal construction that includes nickel and platinum electrodes and a strategically skinny AlScN layer, solely 45 nanometers thick. This configuration helps preserve environment friendly operation whilst temperatures trigger particles inside the materials to maneuver erratically.
This development is not only about enhancing the resilience of reminiscence storage. The researchers envision their know-how enabling extra refined computing in excessive situations, akin to deep-earth drilling or house exploration, the place standard electronics would falter. For instance, their gadget may drastically enhance the effectivity of synthetic intelligence (AI) techniques that at present undergo from knowledge switch bottlenecks between the central processing unit and reminiscence storage.
The group highlights one other important good thing about their invention: by integrating reminiscence and processing models extra carefully, their “memory-enhanced compute” method may remove inefficiencies inherent in conventional computing architectures. This integration may probably enable high-performance computing in environments the place even silicon carbide know-how, an ordinary for high-temperature electronics, falls brief.
The group’s innovation, with its potential to revolutionize fields from geothermal vitality extraction to interplanetary exploration, opens up thrilling prospects for deploying superior computing applied sciences in harsh environments. Their ongoing analysis goals to additional combine this know-how with current high-temperature computing techniques, setting the stage for brand spanking new purposes that require sturdy, high-speed knowledge processing. This might result in vital developments in fields akin to deep-earth drilling, house exploration, and even synthetic intelligence, demonstrating the broad impression of this breakthrough.